Long-term evolution of antibiotic tolerance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections
- PMID: 38045720
- PMCID: PMC10693005
- DOI: 10.1093/evlett/qrad034
Long-term evolution of antibiotic tolerance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections
Abstract
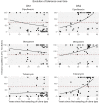
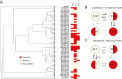
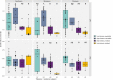
Pathogenic bacteria respond to antibiotic pressure with the evolution of resistance but survival can also depend on their ability to tolerate antibiotic treatment, known as tolerance. While a variety of resistance mechanisms and underlying genetics are well characterized in vitro and in vivo, an understanding of the evolution of tolerance, and how it interacts with resistance in situ is lacking. We assayed for tolerance and resistance in isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from chronic cystic fibrosis lung infections spanning up to 40 years of evolution, with 3 clinically relevant antibiotics: meropenem, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin. We present evidence that tolerance is under positive selection in the lung and that it can act as an evolutionary stepping stone to resistance. However, by examining evolutionary patterns across multiple patients in different clone types, a key result is that the potential for an association between the evolution of resistance and tolerance is not inevitable, and difficult to predict.
Keywords: adaptation; evolutionary medicine; microbial evolutionary genomics.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Society for the Study of Evolution (SSE) and European Society for Evolutionary Biology (ESEN).
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Effects of Antibiotic Combination Treatments on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Tolerance Evolution and Coexistence with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0184222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01842-22. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36453898 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Phenotypic Convergence towards Collateral Sensitivity in Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Presenting Different Genomic Backgrounds.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0227622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02276-22. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36533961 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Antibiotic Tolerance Shapes Resistance Development in Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections.mBio. 2021 Feb 9;12(1):e03482-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03482-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33563834 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic strategies for eradicating Pseudomonas aeruginosa in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 10;(11):CD004197. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004197.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 25;4:CD004197. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004197.pub5 PMID: 25383937 Updated. Review.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa chromosomal beta-lactamase in patients with cystic fibrosis and chronic lung infection. Mechanism of antibiotic resistance and target of the humoral immune response.APMIS Suppl. 2003;(116):1-47. APMIS Suppl. 2003. PMID: 14692154 Review.
Cited by
-
Flagellar motility and the mucus environment influence aggregation mediated antibiotic tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic lung infection.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 25:2024.10.25.620240. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.25.620240. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39484600 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Ultrasound-Mediated Antibiotic Delivery to In Vivo Biofilm Infections: A Review.Chembiochem. 2024 Oct 16;25(20):e202400181. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202400181. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Chembiochem. 2024. PMID: 38924307 Review.
-
Phenotypic resistant single-cell characteristics under recurring ampicillin antibiotic exposure in Escherichia coli.mSystems. 2024 Jul 23;9(7):e0025624. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00256-24. Epub 2024 Jun 26. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38920373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen, S. B., Marvig, R. L., Molin, S., Krogh Johansen, H., & Griffin, A. S. (2015). Long-term social dynamics drive loss of function in pathogenic bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(34), 10756–10761. 10.1073/pnas.1508324112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Auguie, B. (2015). gridExtra: Miscellaneous functions for “Grid” Graphics. R package version 2.0.0. http://cran.r-project.org/package=gridExtra.
-
- Baker, C. N., Stocker, S. A., Culver, D. H., & Thornsberry, C. (1991). Comparison of the E-test to agar dilution, broth microdilution, and agar diffusion susceptibility testing techniques by using a special challenge set of bacteria. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 29(3), 533–538. 10.1128/jcm.29.3.533-538.1991 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

