Anti-virulence and bactericidal activities of Stattic against Shigella sonnei
- PMID: 38032177
- PMCID: PMC10734500
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.01074-23
Anti-virulence and bactericidal activities of Stattic against Shigella sonnei
Abstract
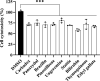
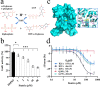
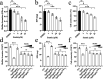
Shigella sonnei is a major human enteric pathogen that causes bacillary dysentery. The increasing spread of drug-resistant S. sonnei strains has caused an emergent need for the development of new antimicrobial agents against this pathogenic bacterium. In this study, we demonstrate that Stattic employs two antibacterial mechanisms against S. sonnei. It exerted both anti-virulence activity and bactericidal activity against S. sonnei, suggesting that it shows advantages over traditional antibiotics. Moreover, Stattic showed excellent synergistic effects with kanamycin, ampicillin, chloramphenicol, and gentamicin against S. sonnei. Our findings suggest that Stattic has promising potential for development as a new antibiotic or as an adjuvant to antibiotics for infections caused by S. sonnei.
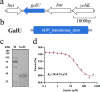
Keywords: GalU; Shigella sonnei; Stattic; antibiotic; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
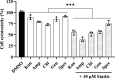
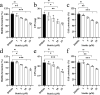
Similar articles
-
[Study of the stability of antibiotic resistance of Shigella sonnei in epidemiologic practice].Antibiotiki. 1974 Dec;19(12):1117-1120. Antibiotiki. 1974. PMID: 4614700 Russian. No abstract available.
-
Epidemiological characterization of resistance and PCR typing of Shigella flexneri and Shigella sonnei strains isolated from bacillary dysentery cases in Southeast Brazil.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007 Feb;40(2):249-58. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2007000200012. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007. PMID: 17273662
-
[Significance of determination of Shigella antibiotic resistance in bacteriological diagnosis of dysentery].Antibiot Khimioter. 2005;50(2-3):30-2. Antibiot Khimioter. 2005. PMID: 16308937 Russian.
-
Shigella sonnei: virulence and antibiotic resistance.Arch Microbiol. 2021 Jan;203(1):45-58. doi: 10.1007/s00203-020-02034-3. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Arch Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 32929595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of Shigella sonnei: A highly drug-resistant pathogen of increasing prevalence.Virulence. 2023 Dec;14(1):2280838. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2023.2280838. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Virulence. 2023. PMID: 37994877 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muthuirulandi Sethuvel DP, Mutreja A, Pragasam AK, Vasudevan K, Murugan D, Anandan S, Michael JS, Walia K, Veeraraghavan B, Rao K. 2020. Phylogenetic and evolutionary analysis reveals the recent dominance of ciprofloxacin-resistant Shigella sonnei and local persistence of S. flexneri clones in India. mSphere 5. doi:10.1128/mSphere.00569-20 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khalil IA, Troeger C, Blacker BF, Rao PC, Brown A, Atherly DE, Brewer TG, Engmann CM, Houpt ER, Kang G, et al. . 2018. Morbidity and mortality due to Shigella and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: the global burden of disease study 1990–2016. Lancet Infect Dis 18:1229–1240. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30475-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lampel KA. 2009. Shigella. In Pathogens and toxins in foods: challenges and interventions
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

