Understanding cellular senescence: pathways involved, therapeutics and longevity aiding
- PMID: 38031713
- PMCID: PMC10730163
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2287929
Understanding cellular senescence: pathways involved, therapeutics and longevity aiding
Abstract
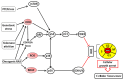
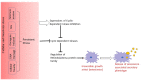
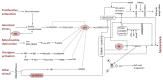
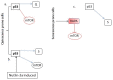
A normal somatic cell undergoes cycles of finite cellular divisions. The presence of surveillance checkpoints arrests cell division in response to stress inducers: oxidative stress from excess free radicals, oncogene-induced abnormalities, genotoxic stress, and telomere attrition. When facing such stress when undergoing these damages, there is a brief pause in the cell cycle to enable repair mechanisms. Also, the nature of stress determines whether the cell goes for repair or permanent arrest. As the cells experience transient or permanent stress, they subsequently choose the quiescence or senescence stage, respectively. Quiescence is an essential stage that allows the arrested/damaged cells to go through appropriate repair mechanisms and then revert to the mainstream cell cycle. However, senescent cells are irreversible and accumulate with age, resulting in inflammation and various age-related disorders. In this review, we focus on senescence-associated pathways and therapeutics understanding cellular senescence as a cascade that leads to aging, while discussing the recent details on the molecular pathways involved in regulating senescence and the benefits of therapeutic strategies against accumulated senescent cells and their secretions.
Keywords: DNA damage; SASP; Senescence; aging; longevity; senolytic.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Using Experience Sampling Methodology to Capture Disclosure Opportunities for Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):389-400. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0090. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116059 Free PMC article.
-
Australia in 2030: what is our path to health for all?Med J Aust. 2021 May;214 Suppl 8:S5-S40. doi: 10.5694/mja2.51020. Med J Aust. 2021. PMID: 33934362
-
Review of Machine Learning Techniques in Soft Tissue Biomechanics and Biomaterials.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2024 Oct;15(5):522-549. doi: 10.1007/s13239-024-00737-y. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2024. PMID: 38956008 Review.
Cited by
-
Aging disrupts the coordination between mRNA and protein expression in mouse and human midbrain.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 1:2024.06.01.596950. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.01.596950. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38854057 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Immunometabolic changes and potential biomarkers in CFS peripheral immune cells revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing.J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 11;22(1):925. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05710-w. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39394558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mattison JA, Colman RJ, Beasley TM, et al. Caloric restriction improves health and survival of rhesus monkeys. Nat Commun. 2017;8 [[cited 2022 Oct 31]]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28094793/ - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pifferi F, Terrien J, Marchal J, et al. Caloric restriction increases lifespan but affects brain integrity in grey mouse lemur primates. Commun Biol Internet. 2018;1 [cited 2022 Oct 31]. /pmc/articles/PMC6123706/ - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
