Kalkitoxin attenuates calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells via RUNX-2 signaling pathways
- PMID: 38031648
- PMCID: PMC10556282
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.23148
Kalkitoxin attenuates calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells via RUNX-2 signaling pathways
Abstract
Background: Kalkitoxin (KT) is an active lipopeptide isolated from the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula found in the bed of the coral reef. Although KT suppresses cell division and inflammation, KT's mechanism of action in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) is unidentified. Therefore, our main aim was to investigate the impact of KT on vascular calcification for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
Objectives: Using diverse calcification media, we studied the effect of KT on VSMC calcification and the underlying mechanism of this effect.
Methods: VSMC was isolated from the 6 weeks ICR mice. Then VSMCs were treated with different concentrations of KT to check the cell viability. Alizarin red and von Kossa staining were carried out to examine the calcium deposition on VSMC. Thoracic aorta of 6 weeks mice were taken and treated with different concentrations of KT, and H and E staining was performed. Real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blot were performed to examine KT's effect on VSMC mineralization. Calcium deposition on VSMC was examined with a calcium deposition quantification kit.
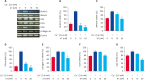
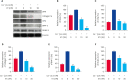
Results: Calcium deposition, Alizarin red, and von Kossa staining revealed that KT reduced inorganic phosphate-induced calcification phenotypes. KT also reduced Ca++-induced calcification by inhibiting genes that regulate osteoblast differentiation, such as runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX-2), SMAD family member 4, osterix, collagen 1α, and osteopontin. Also, KT repressed Ca2+-induced bone morphogenetic protein 2, RUNX-2, collagen 1α, osteoprotegerin, and smooth muscle actin protein expression. Likewise, Alizarin red and von Kossa staining showed that KT markedly decreased the calcification of ex vivo ring formation in the mouse thoracic aorta.
Conclusions: This experiment demonstrated that KT decreases vascular calcification and may be developed as a new therapeutic treatment for vascular calcification and arteriosclerosis.
Keywords: BMP-2; Kalkitoxin; RUNX-2; vascular calcification; vascular smooth muscle cell.
© 2023 The Korean Society of Veterinary Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aloe-emodin inhibits osteogenic differentiation and calcification of mouse vascular smooth muscle cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 15;865:172772. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172772. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31697934
-
Dorsomorphin homologue 1, a highly selective small-molecule bone morphogenetic protein inhibitor, suppresses medial artery calcification.J Vasc Surg. 2017 Aug;66(2):586-593. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.03.462. Epub 2016 Jun 30. J Vasc Surg. 2017. PMID: 27374065 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 attenuates calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;69(12):1802-1816. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12826. Epub 2017 Oct 4. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28980322
-
Vascular Calcification: Molecular Networking, Pathological Implications and Translational Opportunities.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 25;14(3):275. doi: 10.3390/biom14030275. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc Action in Vascular Calcification.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2024 Jun 30;29(2):118-124. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2024.29.2.118. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 38974586 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis and Mechanism of Uremic Vascular Calcification.Cureus. 2024 Jul 17;16(7):e64771. doi: 10.7759/cureus.64771. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39026575 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Badimon L, Badimon JJ, Cohen M, Chesebro JH, Fuster V. Vessel wall-related risk factors in acute vascular events. Drugs. 1991;42(Suppl 5):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Tinkov AA, Filippini T, Ajsuvakova OP, Skalnaya MG, Aaseth J, Bjørklund G, et al. Cadmium and atherosclerosis: a review of toxicological mechanisms and a meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. Environ Res. 2018;162:240–260. - PubMed
-
- Hruska KA, Mathew S, Saab G. Bone morphogenetic proteins in vascular calcification. Circ Res. 2005;97(2):105–114. - PubMed
-
- London GM, Guérin AP, Marchais SJ, Métivier F, Pannier B, Adda H. Arterial media calcification in end-stage renal disease: impact on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18(9):1731–1740. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

