N-linked glycans: an underappreciated key determinant of T cell development, activation, and function
- PMID: 38027254
- PMCID: PMC10662610
- DOI: 10.1097/IN9.0000000000000035
N-linked glycans: an underappreciated key determinant of T cell development, activation, and function
Abstract
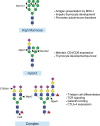
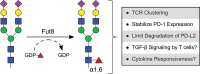
N-linked glycosylation is a post-translational modification that results in the decoration of newly synthesized proteins with diverse types of oligosaccharides that originate from the amide group of the amino acid asparagine. The sequential and collective action of multiple glycosidases and glycosyltransferases are responsible for determining the overall size, composition, and location of N-linked glycans that become covalently linked to an asparagine during and after protein translation. A growing body of evidence supports the critical role of N-linked glycan synthesis in regulating many features of T cell biology, including thymocyte development and tolerance, as well as T cell activation and differentiation. Here, we provide an overview of how specific glycosidases and glycosyltransferases contribute to the generation of different types of N-linked glycans and how these post-translational modifications ultimately regulate multiple facets of T cell biology.
Keywords: N-linked glycans; T cells; glycobiology; glycosylation; immune responses.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s), Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A genetic approach to Mammalian glycan function.Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:643-91. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161809. Epub 2003 Mar 27. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12676797 Review.
-
Protein glycosylation in cancers and its potential therapeutic applications in neuroblastoma.J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Sep 29;9(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0334-6. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27686492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycans as Key Checkpoints of T Cell Activity and Function.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 27;9:2754. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02754. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30538706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How glycosylation affects glycosylation: the role of N-glycans in glycosyltransferase activity.Glycobiology. 2020 Dec 9;30(12):941-969. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwaa041. Glycobiology. 2020. PMID: 32363402 Review.
-
Asparagine-linked oligosaccharides facilitate human chorionic gonadotropin beta-subunit folding but not assembly of prefolded beta with alpha.Endocrinology. 1995 Jan;136(1):52-61. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.1.7530195. Endocrinology. 1995. PMID: 7530195
Cited by
-
The Glycan Ectodomain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Modulates Cytokine Production and Expression of CD206 Mannose Receptor in PBMC Cultures of Pre-COVID-19 Healthy Subjects.Viruses. 2024 Mar 24;16(4):497. doi: 10.3390/v16040497. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trombetta ES, Helenius A. Lectins as chaperones in glycoprotein folding. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998;8(5):587–92. - PubMed
-
- Wormald MR, Dwek RA. Glycoproteins: glycan presentation and protein-fold stability. Structure. 1999;7(7):R155–60. - PubMed
-
- Ohtsubo K, Marth JD. Glycosylation in cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell. 2006;126(5):855–67. - PubMed
-
- Schachter H. The joys of HexNAc. The synthesis and function of N- and O-glycan branches. Glycoconj J. 2000;17(7–9):465–83. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
