The role of primed and non-primed MSC-derived conditioned media in neuroregeneration
- PMID: 38025267
- PMCID: PMC10656692
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1241432
The role of primed and non-primed MSC-derived conditioned media in neuroregeneration
Abstract
Introduction: With growing significance in nervous system repair, mesenchymal stem cell-derived conditioned media (MSCCM) have been used in cell-free therapies in regenerative medicine. However, the immunomodulatory and neuroregenerative effects of MSCCM and the influence of priming on these effects are still poorly understood.
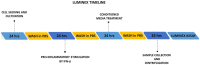
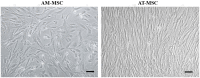
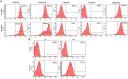
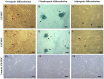
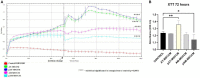
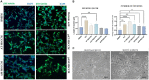
Methods: In this study, by various methods focused on cell viability, proliferation, neuron-like differentiation, neurite outgrowth, cell migration and regrowth, we demonstrated that MSCCM derived from adipose tissue (AT-MSCCM) and amniotic membrane (AM-MSCCM) had different effects on SH-SY5Y cells.
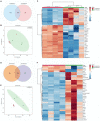
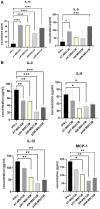
Results and discussion: AT-MSCCM was found to have a higher proliferative capacity and the ability to impact neurite outgrowth during differentiation, while AM-MSCCM showed more pronounced immunomodulatory activity, migration, and re-growth of SH-SY5Y cells in the scratch model. Furthermore, priming of MSC with pro-inflammatory cytokine (IFN-γ) resulted in different proteomic profiles of conditioned media from both sources, which had the highest effect on SH-SY5Y proliferation and neurite outgrowth in terms of the length of neurites (pAT-MSCCM) compared to the control group (DMEM). Altogether, our results highlight the potential of primed and non-primed MSCCM as a therapeutic tool for neurodegenerative diseases, although some differences must be considered.
Keywords: IFN-γ; MSC; conditioned medium; neurotrophic effect; priming.
Copyright © 2023 Hudakova, Mudronova, Marcincakova, Slovinska, Majerova, Maloveska, Petrouskova, Humenik and Cizkova.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of mesenchymal stem cells derived conditioned media on neural progenitor cells.Gen Physiol Biophys. 2021 Nov;40(6):551-559. doi: 10.4149/gpb_2021026. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2021. PMID: 34897026
-
A comparison of high-content screening versus manual analysis to assay the effects of mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium on neurite outgrowth in vitro.J Biomol Screen. 2010 Jun;15(5):576-82. doi: 10.1177/1087057110367959. Epub 2010 Apr 16. J Biomol Screen. 2010. PMID: 20400727
-
Effects of Stromal Cell Conditioned Medium and Antipurinergic Treatment on Macrophage Phenotype.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022 Dec;28(12):656-671. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2022.0123. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022. PMID: 36329666 Free PMC article.
-
Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: An Intriguing Approach for Neuroprotection and Neuroregeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 31;23(1):456. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010456. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium: An Attractive Alternative for Regenerative Therapy.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019 Feb;25(1):78-88. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2018.0168. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019. PMID: 30156475 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

