Impaired synaptic incorporation of AMPA receptors in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome
- PMID: 38025260
- PMCID: PMC10665894
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1258615
Impaired synaptic incorporation of AMPA receptors in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome
Abstract
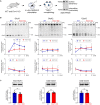
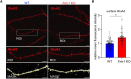
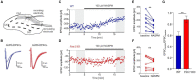
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is the most common monogenetic cause of inherited intellectual disability and autism in humans. One of the well-characterized molecular phenotypes of Fmr1 KO mice, a model of FXS, is increased translation of synaptic proteins. Although this upregulation stabilizes in adulthood, abnormalities during the critical period of plasticity have long-term effects on circuit formation and synaptic properties. Using high-resolution quantitative proteomics of synaptoneurosomes isolated from the adult, developed brains of Fmr1 KO mice, we show a differential abundance of proteins regulating the postsynaptic receptor activity of glutamatergic synapses. We investigated the AMPA receptor composition and shuttling in adult Fmr1 KO and WT mice using a variety of complementary experimental strategies such as surface protein crosslinking, immunostaining of surface receptors, and electrophysiology. We discovered that the activity-dependent synaptic delivery of AMPARs is impaired in adult Fmr1 KO mice. Furthermore, we show that Fmr1 KO synaptic AMPARs contain more GluA2 subunits that can be interpreted as a switch in the synaptic AMPAR subtype toward an increased number of Ca2+-impermeable receptors in adult Fmr1 KO synapses.
Keywords: AMPA receptors; FXS; Fmr1 KO; GluA2; brain; synaptic plasticity.
Copyright © 2023 Chojnacka, Beroun, Magnowska, Stawikowska, Cysewski, Milek, Dziembowska and Kuzniewska.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transient Enhanced GluA2 Expression in Young Hippocampal Neurons of a Fragile X Mouse Model.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020 Dec 3;12:588295. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2020.588295. eCollection 2020. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33343326 Free PMC article.
-
Altered structural and functional synaptic plasticity with motor skill learning in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome.J Neurosci. 2013 Dec 11;33(50):19715-23. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2514-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24336735 Free PMC article.
-
CPEB3-dependent increase in GluA2 subunits impairs excitatory transmission onto inhibitory interneurons in a mouse model of fragile X.Cell Rep. 2022 Jun 7;39(10):110853. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110853. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35675768 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptor Signaling in Neural Progenitors Modeling Fragile X Syndrome.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2019 Feb 8;11:2. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2019.00002. eCollection 2019. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30800064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling fragile X syndrome in the Fmr1 knockout mouse.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2014 Nov;3(4):118-33. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2014.01024. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2014. PMID: 25606362 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

