Readministration of high-dose adeno-associated virus gene therapy vectors enabled by ImmTOR nanoparticles combined with B cell-targeted agents
- PMID: 38024395
- PMCID: PMC10673641
- DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad394
Readministration of high-dose adeno-associated virus gene therapy vectors enabled by ImmTOR nanoparticles combined with B cell-targeted agents
Abstract
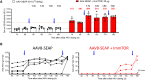
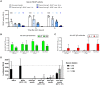
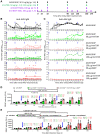
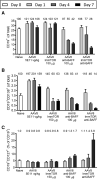
Tolerogenic ImmTOR nanoparticles encapsulating rapamycin have been demonstrated to mitigate immunogenicity of adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene therapy vectors, enhance levels of transgene expression, and enable redosing of AAV at moderate vector doses of 2 to 5E12 vg/kg. However, recent clinical trials have often pushed AAV vector doses 10-fold to 50-fold higher, with serious adverse events observed at the upper range. Here, we assessed combination therapy of ImmTOR with B cell-targeting drugs for the ability to increase the efficiency of redosing at high vector doses. The combination of ImmTOR with a monoclonal antibody against B cell activation factor (aBAFF) exhibited strong synergy leading to more than a 5-fold to 10-fold reduction of splenic mature B cells and plasmablasts while increasing the fraction of pre-/pro-B cells. In addition, this combination dramatically reduced anti-AAV IgM and IgG antibodies, thus enabling four successive AAV administrations at doses up to 5E12 vg/kg and at least two AAV doses at 5E13 vg/kg, with the transgene expression level in the latter case being equal to that observed in control animals receiving a single vector dose of 1E14 vg/kg. Similar synergistic effects were seen with a combination of ImmTOR and a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor, ibrutinib. These results suggest that ImmTOR could be combined with B cell-targeting agents to enable repeated vector administrations as a potential strategy to avoid toxicities associated with vector doses above 1E14 vg/kg.
Keywords: AAV redosing; adeno-associated virus; gene therapy; immune tolerance; immunogenicity.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of National Academy of Sciences.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ImmTOR nanoparticles enhance AAV transgene expression after initial and repeat dosing in a mouse model of methylmalonic acidemia.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021 Jul 16;22:279-292. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2021.06.015. eCollection 2021 Sep 10. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021. PMID: 34485611 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of liver-directed transgene expression at initial and repeat doses of AAV vectors admixed with ImmTOR nanoparticles.Sci Adv. 2021 Feb 24;7(9):eabd0321. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abd0321. Print 2021 Feb. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33627416 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin nanoparticles increase the therapeutic window of engineered interleukin-2 and drive expansion of antigen-specific regulatory T cells for protection against autoimmune disease.J Autoimmun. 2023 Nov;140:103125. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103125. Epub 2023 Oct 14. J Autoimmun. 2023. PMID: 37844543
-
Development of ImmTOR Tolerogenic Nanoparticles for the Mitigation of Anti-drug Antibodies.Front Immunol. 2020 May 20;11:969. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00969. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32508839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunogenicity and toxicity of AAV gene therapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 12;13:975803. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.975803. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032092 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
rAAV expressing a COBRA-designed influenza hemagglutinin generates a protective and durable adaptive immune response with a single dose.J Virol. 2024 Aug 20;98(8):e0078124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00781-24. Epub 2024 Jul 30. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39078191
-
Role of FoxP3+ Regulatory T Cells in Modulating Immune Responses to Adeno-Associated Virus Gene Therapy.Hum Gene Ther. 2024 Jul;35(13-14):439-450. doi: 10.1089/hum.2023.227. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Hum Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38450566 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

