Metformin Caused Radiosensitivity of Breast Cancer Cells through the Expression Modulation of miR-21-5p/SESN1axis
- PMID: 38019229
- PMCID: PMC10772753
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.11.3715
Metformin Caused Radiosensitivity of Breast Cancer Cells through the Expression Modulation of miR-21-5p/SESN1axis
Abstract
Objective: In this research we evaluated molecular mechanism of effect of metformin in radio sensitivity of breast cancer cells.
Methods: This research was done in cellular and molecular research center of Qazvin university of Medical science in 1399 to 1401. Studied samples were two breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) they are derived from primary and secondary tumors resected from a single patient. We exposed them to cumulative 50 Gy radiation and constructed radio resistant cell lines. Then resistant cell lines were treated with 50µm of metformin. Our studied groups were resistant cells treated and un treated with metformin. Then, the expression rate of miR-21-5p and SESN1 gene in resistant and control cells was checked by Quantitative Real-time PCR(qRTPCR). After the cell lines were treated with different concentrations of metformin at different intervals, the rate of cell proliferation and cell death was checked by CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry. The Western blot method was also used to confirm the expression of some genes.
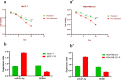
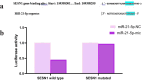
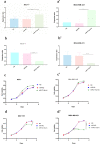
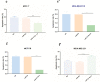
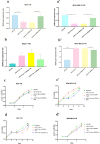
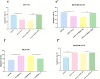
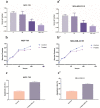
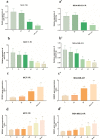
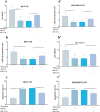
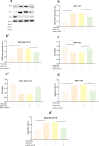
Results: Our results showed that the expression of miR-21-5p was upregulated in radiation-resistant cancer cells (1.8±0.65) (P<0.0001) MCF-7 cell line and (1.6±0.42)(P<0.001) MBA-MD-231 cell line, while the expression of SESN1 was down regulated (0.46±0.12) (P<0.0001) MCF-7 cell line and (0.42±0.22) (P<0.001) MBA-MD-231 cell line. Metformin enhanced the radio sensitivity of breast cancer cells in a dose and time-dependent manner. Also, metformin treatment decreased the expression of miR-21-5p (0.47±0.32) (P<0.0001) MCF-7 Cell line and (0.45±0.21)(P<0.001) MBA-MD-231 cell line and increased the expression of SESN1 (1.65±0.72)(P<0.0001)MCF-7 cell line and (1.73±0.52)(P<0.0001) MBA-MD-231 cell line. The function of metformin was reversed by miR-21-5p inhibitors or the transfection of SESN1 overexpressing plasmids.
Conclusion: In conclusion, based on this research results, metformin enhanced the radio sensitivity of breast cancer cells via modulating the expression of miR-21-5p and SESN1.
Keywords: Metformin; Radio resistant; SESN1 gene; breast cancer; miR-21-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation of miR-93-5p and its effect on the radiosensitivity of breast cancer.Cell Cycle. 2021 Jun;20(12):1173-1180. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1930356. Epub 2021 May 24. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34024254 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells through the regulation of miR-16-5p/WEE1 axis.IUBMB Life. 2020 May;72(5):1012-1022. doi: 10.1002/iub.2242. Epub 2020 Feb 6. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 32027086
-
Cisplatin-resistant MDA-MB-231 Cell-derived Exosomes Increase the Resistance of Recipient Cells in an Exosomal miR-423-5p-dependent Manner.Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(10):804-814. doi: 10.2174/1389200220666190819151946. Curr Drug Metab. 2019. PMID: 31424364
-
mir-129-5p Attenuates Irradiation-Induced Autophagy and Decreases Radioresistance of Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting HMGB1.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Dec 31;21:4122-9. doi: 10.12659/msm.896661. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26720492 Free PMC article.
-
miR-27a-mediated antiproliferative effects of metformin on the breast cancer cell line MCF-7.Oncol Rep. 2016 Dec;36(6):3691-3699. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5199. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27779715
Cited by
-
Metformin: From Diabetes to Cancer-Unveiling Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies.Biology (Basel). 2024 Apr 27;13(5):302. doi: 10.3390/biology13050302. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38785784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alimova IN. Metformin inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:909–15. - PubMed
-
- Chevalier B, Pasquier D, Lartigau EF, et al. Metformin: (future) best friend of the radiation oncologist? Radio Ther Oncol. 2020;151:95–105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

