METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation induces the differentiation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblasts via the miR-21/PTEN pathway
- PMID: 38017523
- PMCID: PMC10683095
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-023-02606-z
METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation induces the differentiation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblasts via the miR-21/PTEN pathway
Abstract
Background: The accumulation of myofibroblasts is the key pathological feature of pulmonary fibrosis (PF). Aberrant differentiation of lung-resident mesenchymal stem cells (LR-MSCs) has been identified as a critical source of myofibroblasts, but the molecular mechanisms underlying this process remain largely unknown. In recent years, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification has been implicated in fibrosis development across diverse organs; however, its specific role in promoting the differentiation of LR-MSCs into myofibroblasts in PF is not well defined.
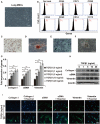
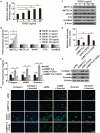
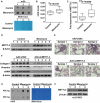
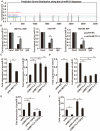
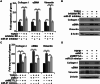
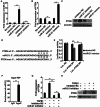
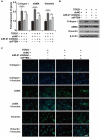
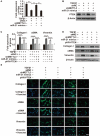
Methods: In this study, we examined the levels of m6A RNA methylation and the expression of its regulatory enzymes in both TGF-β1-treated LR-MSCs and fibrotic mouse lung tissues. The downstream target genes of m6A and their related pathways were identified according to a literature review, bioinformatic analysis and experimental verification. We also assessed the expression levels of myofibroblast markers in treated LR-MSCs and confirmed the involvement of the above-described pathway in the aberrant differentiation direction of LR-MSCs under TGF-β1 stimulation by overexpressing or knocking down key genes within the pathway.
Results: Our results revealed that METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation was significantly upregulated in both TGF-β1-treated LR-MSCs and fibrotic mouse lung tissues. This process directly led to the aberrant differentiation of LR-MSCs into myofibroblasts by targeting the miR-21/PTEN pathway. Moreover, inhibition of METTL3 or miR-21 and overexpression of PTEN could rescue this abnormal differentiation.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that m6A RNA methylation induced aberrant LR-MSC differentiation into myofibroblasts via the METTL3/miR-21/PTEN signaling pathway. We indicated a novel mechanism to promote PF progression. Targeting METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation and its downstream targets may present innovative therapeutic approaches for the prevention and treatment of PF.
Keywords: Lung resident mesenchymal stem cells (LR-MSCs); M6A methylation; METTL3/miR-21/PTEN pathway; Myofibroblast; Pulmonary fibrosis (PF).
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-124 regulates transforming growth factor-β1 induced differentiation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells to myofibroblast by repressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Dev Biol. 2019 May 15;449(2):115-121. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30802451
-
SENP1 regulates the transformation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells and is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis progression.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Jul 14;20(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00921-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35836260 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β1-induced miR-424 promotes pulmonary myofibroblast differentiation by targeting Slit2 protein expression.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;180:114172. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114172. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32712053 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Lung Resident Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in the Pathogenesis and Repair of Chronic Lung Disease.Stem Cells. 2023 May 15;41(5):431-443. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxad014. Stem Cells. 2023. PMID: 36749355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genesis of the myofibroblast in lung injury and fibrosis.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2012 Jul;9(3):148-52. doi: 10.1513/pats.201201-011AW. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2012. PMID: 22802289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revisiting the role of MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 16;12:1470875. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1470875. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39479511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL3 accelerates staphylococcal protein A (SpA)-induced osteomyelitis progression by regulating m6A methylation-modified miR-320a.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Nov 6;19(1):729. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05164-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39506767 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of RRBP1 mRNA via an m6A-dependent manner in prostate cancer constitutes a therapeutic vulnerability amenable to small-peptide inhibition of METTL3.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Oct 5;81(1):414. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05418-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39367907 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a cross-talk between TGF-β signaling and MicroRNAs.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 25;11:1415278. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1415278. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39386739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell-based therapy for fibrotic diseases: mechanisms and pathways.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jun 18;15(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03782-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38886859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

