Transpulmonary Expression of Exosomal microRNAs in Idiopathic and Congenital Heart Disease-Related Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 38014665
- PMCID: PMC10727351
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.123.031435
Transpulmonary Expression of Exosomal microRNAs in Idiopathic and Congenital Heart Disease-Related Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH) is a fatal disease characterized by a complex pathogenesis. Exosomes containing microRNAs (miRs) have emerged as a novel biomarker. Transpulmonary exosomal miRs offer valuable insights into pulmonary circulation microenvironments. Hereby, we aimed to explore the potentials of transpulmonary exosomal miRs as differentiating factors between idiopathic PAH and congenital heart disease (CHD)-related PAH.
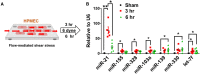
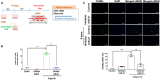
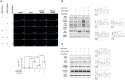
Methods and results: During right heart catheterization, we collected exosomes at pulmonary arteries in 25 patients diagnosed with idiopathic PAH and 20 patients with CHD-related PAH. Next-generation sequencing identified several candidate exosomal miRs. Using quantitative polymerase chain reaction, we validated the expressions of these miRs and revealed significantly elevated expressions of miR-21, miR-139-5p, miR-155-5p, let-7f-5p, miR-328-3p, miR-330-3p, and miR-103a-3p in patients with CHD-related PAH, in contrast to patients with idiopathic PAH. Among these miRs, miR-21 exhibited the highest expression in patients with CHD-related PAH. These findings were further corroborated in an external cohort comprising 10 patients with idiopathic PAH and 8 patients with CHD-related PAH. Using an in vitro flow model simulating the shear stress experienced by pulmonary endothelial cells, we observed a significant upregulation of miR-21. Suppressing miR-21 rescued the shear stress-induced downregulation of the RAS/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway, leading to a mitigation of apoptosis.
Conclusions: Our study identified a pronounced expression of transpulmonary exosomal miR-21, particularly in patients with CHD-related PAH, through next-generation sequencing analysis. Further investigation is warranted to elucidate the regulatory mechanisms involving miR-21 in the pathophysiology of PAH.
Keywords: congenital heart disease; exosome microRNAs; pulmonary artery hypertension; transpulmonary expression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MircoRNA in Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Alters Endothelial Angiogenic Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 8;23(19):11964. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911964. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233263 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying microRNAs targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in end-stage idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Aug;94(8):875-85. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1426-z. Epub 2016 May 18. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27188753 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and clinical significance of miR-8078 in patients with congenital heart disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension.Gene. 2024 Feb 20;896:147964. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147964. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Gene. 2024. PMID: 37926175
-
Recent progress in the roles of microRNAs in pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with congenital heart disease.Narra J. 2024 Apr;4(1):e579. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i1.579. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 38798867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic angiogenesis with exosomal microRNAs: an effectual approach for the treatment of myocardial ischemia.Heart Fail Rev. 2021 Jan;26(1):205-213. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-10001-9. Heart Fail Rev. 2021. PMID: 32632768 Review.
Cited by
-
Variation and significance of serum microRNA-21 level in pediatric pulmonary artery hypertension associated with congenital heart disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Sep 5;11:1424679. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1424679. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39309603 Free PMC article.
-
Global research landscape on the genetics of congenital heart disease: A bibliometric and visualized analysis via VOSviewer and CiteSpace.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 25;103(43):e40261. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040261. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39470501 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Biomarkers in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: An Update.Biomolecules. 2024 May 3;14(5):552. doi: 10.3390/biom14050552. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785959 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

