This is a preprint.
Identification of Cellular Interactions in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment Underlying CD8 T Cell Exhaustion
- PMID: 38014233
- PMCID: PMC10680664
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.09.566384
Identification of Cellular Interactions in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment Underlying CD8 T Cell Exhaustion
Abstract
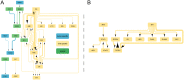
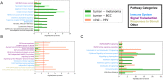
While immune checkpoint inhibitors show success in treating a subset of patients with certain late-stage cancers, these treatments fail in many other patients as a result of mechanisms that have yet to be fully characterized. The process of CD8 T cell exhaustion, by which T cells become dysfunctional in response to prolonged antigen exposure, has been implicated in immunotherapy resistance. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) produces an abundance of data to analyze this process; however, due to the complexity of the process, contributions of other cell types to a process within a single cell type cannot be simply inferred. We constructed an analysis framework to first rank human skin tumor samples by degree of exhaustion in tumor-infiltrating CD8 T cells and then identify immune cell type-specific gene-regulatory network patterns significantly associated with T cell exhaustion. Using this framework, we further analyzed scRNA-seq data from human tumor and chronic viral infection samples to compare the T cell exhaustion process between these two contexts. In doing so, we identified transcription factor activity in the macrophages of both tissue types associated with this process. Our framework can be applied beyond the tumor immune microenvironment to any system involving cell-cell communication, facilitating insights into key biological processes that underpin the effective treatment of cancer and other complicated diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals TOX as a promoting factor for T cell exhaustion and a predictor for anti-PD-1 responses in human cancer.Genome Med. 2020 Feb 28;12(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13073-020-00722-9. Genome Med. 2020. PMID: 32111241 Free PMC article.
-
Exhausted CD8+T Cells in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment: New Pathways to Therapy.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 2;11:622509. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.622509. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33633741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reinvigorating exhausted CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the tumor microenvironment and current strategies in cancer immunotherapy.Med Res Rev. 2021 Jan;41(1):156-201. doi: 10.1002/med.21727. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Med Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 32844499 Review.
-
Identification and validation of a novel signature based on cell-cell communication in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by integrated analysis of single-cell transcriptome and bulk RNA-sequencing.Front Oncol. 2023 May 5;13:1136729. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1136729. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37213285 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Cbl-b inhibits CD8+ T-cell exhaustion and promotes CAR T-cell function.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jan;9(1):e001688. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001688. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33462140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gibellini L., De Biasi S., Porta C., Lo Tartaro D., Depenni R., Pellacani G., Sabbatini R., and Cossarizza A.. Single-cell approaches to profile the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front Immunol, 11:490, 2020. 2020/04/09 Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 20;11:490. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00490. eCollection 2020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blank C. U., Haining W. N., Held W., Hogan P. G., Kallies A., Lugli E., Lynn R. C., Philip M., Rao A., Restifo N. P., Schietinger A., Schumacher T. N., Schwartzberg P. L., Sharpe A. H., Speiser D. E., Wherry E. J., Youngblood B. A., and Zehn D.. Defining ‘t cell exhaustion’. Nat Rev Immunol, 19(11):665–674, 2019. 2019/10/02 Nat Rev Immunol. 2019 Nov;19(11):665–674. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0221-9. Epub 2019 Sep 30. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
