Mapping the intersection of nanotechnology and SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 38013718
- PMCID: PMC9233748
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imj.2022.06.005
Mapping the intersection of nanotechnology and SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has imposed great medical and economic burdens on human society, and nanotechnology is a promising technique for managing the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. To drive further studies on anti-COVID-19 nanotechnology, this paper provides an analysis, from a bibliometric perspective, of the intersection of nanotechnology and SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19.
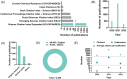
Methods: We analyzed the 2585 publications on nanotechnology and SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 included in the Web of Science Core Collection from January 2019 to March 2022 to determine the bibliometric landscape. The basic bibliometric characteristics are summarized in this article.
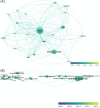
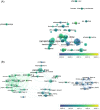
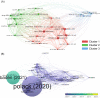
Results: Our bibliometric analysis revealed that the intersection between nanotechnology and SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 is a cutting-edge field in the science community and that the related studies were multidisciplinary in nature. Studies on the structural basis of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-2 detection assays, and mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 provided the development foundation for this field.
Conclusions: The current research focuses are the development of nanomaterial-based vaccines and SARS-CoV-2 detection methods, and the design of nanomedicines carrying SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors is a relatively burgeoning frontier. In summary, this bibliometric analysis of the intersection of nanotechnology and SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 highlights the current research focuses of this field to inspire future studies on anti-COVID-19 nanotechnologies.
Keywords: Bibiometric analysis; COVID-19; Coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19; Nano technology; SARS-CoV-2; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, SARS-CoV-2; Web of Science.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of Tsinghua University Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Applications of separation technology in novel coronavirus research, epidemic prevention and detection].Se Pu. 2021 Jul 8;39(7):679-685. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.03022. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34227364 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Scars of COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis of post-COVID-19 fibrosis.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 20;10:967829. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.967829. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36203683 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Patents and Advances on Nanotechnologies against Coronavirus.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2021;15(4):322-330. doi: 10.2174/1872210514666201110125536. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33172382 Review.
-
Nanotechnology-Based Strategies for the Management of COVID-19: Recent Developments and Challenges.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(41):4197-4211. doi: 10.2174/1381612827666210830105459. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 34459371 Review.
-
A bibliometric analysis of rheumatology and COVID-19 researches.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Nov;40(11):4735-4740. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05844-y. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34215906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yin Y., Su W., Zhang J., et al. Separable microneedle patch to protect and deliver DNA nanovaccines against COVID-19. Acs Nano. 2021;15:14347–14359. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

