Screening and identification of key biomarkers associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and depression using bioinformatics
- PMID: 38013317
- PMCID: PMC10681454
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036265
Screening and identification of key biomarkers associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and depression using bioinformatics
Abstract
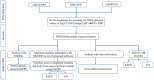
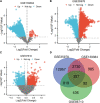
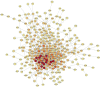
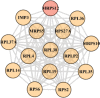
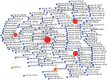
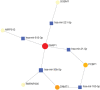
This study aims to identify common molecular biomarkers between amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and depression using bioinformatics methods, in order to provide potential targets and new ideas and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of these diseases. Microarray datasets GSE139384, GSE35978 and GSE87610 were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between ALS and depression were identified. After screening for overlapping DEGs, gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses were performed. Furthermore, a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed using the STRING database and Cytoscape software, and hub genes were identified. Finally, a network between miRNAs and hub genes was constructed using the NetworkAnalyst tool, and possible key miRNAs were predicted. A total of 357 genes have been identified as common DEGs between ALS and depression. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses of the 357 DEGs showed that they were mainly involved in cytoplasmic translation. Further analysis of the PPI network using Cytoscape and MCODE plugins identified 6 hub genes, including mitochondrial ribosomal protein S12 (MRPS12), poly(rC) binding protein 1 (PARP1), SNRNP200, PCBP1, small G protein signaling modulator 1 (SGSM1), and DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1). Five possible target miRNAs, including miR-221-5p, miR-21-5p, miR-100-5p, miR-30b-5p, and miR-615-3p, were predicted by constructing a miRNA-gene network. This study used bioinformatics techniques to explore the potential association between ALS and depression, and identified potential biomarkers. These biomarkers may provide new ideas and methods for the early diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of ALS and depression.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Three hematologic/immune system-specific expressed genes are considered as the potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis through bioinformatics analysis.J Transl Med. 2021 Jan 6;19(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02689-y. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33407587 Free PMC article.
-
Study on potential differentially expressed genes in stroke by bioinformatics analysis.Neurol Sci. 2022 Feb;43(2):1155-1166. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05470-1. Epub 2021 Jul 27. Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34313877 Free PMC article.
-
Key Genes Associated with Pyroptosis in Gout and Construction of a miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network.Cells. 2022 Oct 17;11(20):3269. doi: 10.3390/cells11203269. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291136 Free PMC article.
-
Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Skeletal Muscle Transcriptome Analysis: A Comprehensive Examination of Differentially Expressed Genes.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 20;14(3):377. doi: 10.3390/biom14030377. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Significance of microRNA Biomarkers in ALS-Innocent Bystanders or Disease Culprits?Front Neurol. 2019 Jun 11;10:578. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00578. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31244752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression Changes of miRNAs in Humans and Animal Models of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Their Potential Application for Clinical Diagnosis.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 6;14(9):1125. doi: 10.3390/life14091125. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337908 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Es MA, Hardiman O, Chio A, et al. . Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet. 2017;390:2084–98. - PubMed
-
- Brown RH, Al-Chalabi A. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:162–72. - PubMed
-
- Mitropoulos K, Katsila T, Patrinos GP, et al. . Multi-omics for biomarker discovery and target validation in biofluids for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis diagnosis. OMICS. 2018;22:52–64. - PubMed
-
- Pasinetti GM, Ungar LH, Lange DJ, et al. . Identification of potential CSF biomarkers in ALS. Neurology. 2006;66:1218–22. - PubMed
-
- Blasco H, Vourc’h P, Pradat PF, et al. . Further development of biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2016;16:853–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

