Prevalence and predictors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients worldwide, systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38012781
- PMCID: PMC10683270
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-023-01202-x
Prevalence and predictors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients worldwide, systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Diabetes is a complicated, chronic condition that requires ongoing medical attention as well as multiple risk-reduction measures beyond glucose control. The prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is highly variable in different parts of the world due to various environmental, ethnic, socioeconomic, and rural-urban differences. Diabetes is the leading cause of CKD. This study aimed to estimate the global prevalence of CKD and its associated factors among type 2 diabetes(T2DM) patients, provide scientific evidence for a better understanding of the burden of CKD among diabetes mellitus type 2 patients, and design interventional strategies.
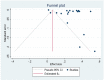
Methods: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) checklist guideline was followed for this review and meta-analysis. The electronic databases (Pub Med, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, and grey literature) were searched to retrieve articles by using keywords. Joanna Briggs Institute Meta-Analysis of Statistics Assessment and Review Instrument was used to assess the quality of studies. The meta-analysis was conducted using STATA 17 software. The Meta logistic regression was computed to present the pooled prevalence and Odds ratio (OR) of the determinate factors with a 95% confidence interval (CI).
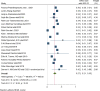
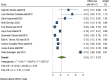
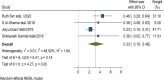
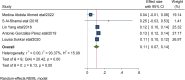
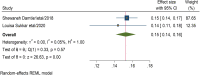
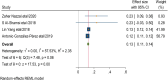
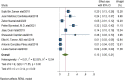
Results: In this systematic review and meta-analysis 20 studies were done in 13 different countries. The pooled magnitude of chronic kidney disease among type 2 DM patients was 27% (95% CI 21%, 33%). The prevalence of chronic kidney disease differs across countries, with the maximum in the USA and the lowest in the United Arab Emirates. Patients with CKD have an elevated risk of severe renal and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists, and, more recently, non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists are among the medications that have been demonstrated to slow the progression of CKD. In this systematic review and meta-analysis increased age, obesity, having a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, smoking history, presence of hypertension, and cardiac heart disease were factors significantly associated with the presence of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients.
Conclusions: The prevalence of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients was high based on the included 20 articles. The review reported that old age, hypertension, cardiac disease, smoking, obesity, and duration of diabetes mellitus was predictor variable for chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients. Therefore, in order to lower the morbidity and mortality from chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients, it is advised to develop both preventive and curative intervention strategies, such as raising awareness, creating a supportive environment, and prescribing appropriate medication at an early stage.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Meta-analysis; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Burden and Determinants of Chronic Kidney Disease Among Diabetic Patients in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Public Health Rev. 2021 Apr 9;42:1603969. doi: 10.3389/phrs.2021.1603969. eCollection 2021. Public Health Rev. 2021. PMID: 34692175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and aldosterone antagonists, in addition to renin-angiotensin system antagonists, on major adverse kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022 Nov;24(11):2159-2168. doi: 10.1111/dom.14801. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022. PMID: 35712807
-
Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: The Canadian REgistry of Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetes Outcomes (CREDO) Study.Clin Ther. 2021 Sep;43(9):1558-1573. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.07.015. Epub 2021 Aug 21. Clin Ther. 2021. PMID: 34426012
-
Behavioral and Pharmacotherapy Weight Loss Interventions to Prevent Obesity-Related Morbidity and Mortality in Adults: An Updated Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Sep. Report No.: 18-05239-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Sep. Report No.: 18-05239-EF-1. PMID: 30354042 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Sudoscan's Effectiveness in Identifying Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.Cureus. 2024 May 15;16(5):e60344. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60344. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38883096 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in predictive modelling of chronic kidney disease: A narrative review.World J Nephrol. 2024 Sep 25;13(3):97214. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v13.i3.97214. World J Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39351189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of HbA1c Estimation Using Immunoturbidimetry and High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Methods in Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.EJIFCC. 2024 Oct 30;35(3):195-205. eCollection 2024 Oct. EJIFCC. 2024. PMID: 39507575 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Biopsy and Immuno-Rheumatological Diseases: A Retrospective and Observational Study.J Pers Med. 2024 Jan 13;14(1):92. doi: 10.3390/jpm14010092. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38248794 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of renal protective gut microbiome derived-metabolites in diabetic chronic kidney disease: An integrated approach using network pharmacology and molecular docking.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2024 Aug;31(8):104028. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2024.104028. Epub 2024 May 23. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38854894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goyal R, Jialal I. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL); 2022; 2022.
-
- Levey AS. Coresh JJTl. Chronic Kidney Disease. 2012;379(9811):165–80. - PubMed
-
- Poretsky L. Principles of Diabetes Mellitus. Springer; 2010.
-
- Cheng AY, Gomes MB, Kalra S, Kengne A-P, Mathieu C, Shaw JEJNRE. Applying the WHO global targets for diabetes mellitus. 2023:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

