Synaptotagmin-7 outperforms synaptotagmin-1 to promote the formation of large, stable fusion pores via robust membrane penetration
- PMID: 38012142
- PMCID: PMC10681989
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42497-8
Synaptotagmin-7 outperforms synaptotagmin-1 to promote the formation of large, stable fusion pores via robust membrane penetration
Abstract
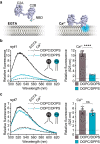
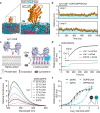
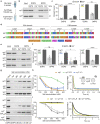
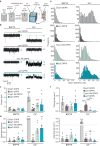
Synaptotagmin-1 and synaptotagmin-7 are two prominent calcium sensors that regulate exocytosis in neuronal and neuroendocrine cells. Upon binding calcium, both proteins partially penetrate lipid bilayers that bear anionic phospholipids, but the specific underlying mechanisms that enable them to trigger exocytosis remain controversial. Here, we examine the biophysical properties of these two synaptotagmin isoforms and compare their interactions with phospholipid membranes. We discover that synaptotagmin-1-membrane interactions are greatly influenced by membrane order; tight packing of phosphatidylserine inhibits binding due to impaired membrane penetration. In contrast, synaptotagmin-7 exhibits robust membrane binding and penetration activity regardless of phospholipid acyl chain structure. Thus, synaptotagmin-7 is a super-penetrator. We exploit these observations to specifically isolate and examine the role of membrane penetration in synaptotagmin function. Using nanodisc-black lipid membrane electrophysiology, we demonstrate that membrane penetration is a critical component that underlies how synaptotagmin proteins regulate reconstituted, exocytic fusion pores in response to calcium.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Allosteric stabilization of calcium and phosphoinositide dual binding engages several synaptotagmins in fast exocytosis.Elife. 2022 Aug 5;11:e74810. doi: 10.7554/eLife.74810. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35929728 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate drives Ca2+-independent membrane penetration by the tandem C2 domain proteins synaptotagmin-1 and Doc2β.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jul 12;294(28):10942-10953. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007929. Epub 2019 May 30. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31147445 Free PMC article.
-
Push-and-pull regulation of the fusion pore by synaptotagmin-7.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 2;107(44):19032-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014070107. Epub 2010 Oct 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20956309 Free PMC article.
-
Role of synaptotagmin in Ca2+-triggered exocytosis.Biochem J. 2002 Aug 15;366(Pt 1):1-13. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020776. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12047220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptotagmin in Ca2+ -dependent exocytosis: dynamic action in a flash.Neuron. 2003 May 22;38(4):521-4. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00290-3. Neuron. 2003. PMID: 12765604 Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptotagmin 7 C2 domains induce membrane curvature stress via electrostatic interactions and the wedge mechanism.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 12:2024.01.10.575084. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.10.575084. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38313280 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

