Signaling pathways and targeted therapies for psoriasis
- PMID: 38008779
- PMCID: PMC10679229
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01655-6
Signaling pathways and targeted therapies for psoriasis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Signaling pathways and targeted therapies for psoriasis.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Jan 22;9(1):25. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01733-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38253486 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
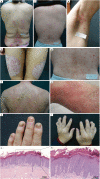
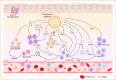
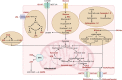
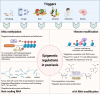
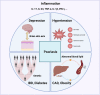
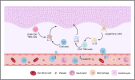
Psoriasis is a common, chronic, and inflammatory skin disease with a high burden on individuals, health systems, and society worldwide. With the immunological pathologies and pathogenesis of psoriasis becoming gradually revealed, the therapeutic approaches for this disease have gained revolutionary progress. Nevertheless, the mechanisms of less common forms of psoriasis remain elusive. Furthermore, severe adverse effects and the recurrence of disease upon treatment cessation should be noted and addressed during the treatment, which, however, has been rarely explored with the integration of preliminary findings. Therefore, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms behind psoriasis pathogenesis, which might offer new insights for research and lead to more substantive progress in therapeutic approaches and expand clinical options for psoriasis treatment. In this review, we looked to briefly introduce the epidemiology, clinical subtypes, pathophysiology, and comorbidities of psoriasis and systematically discuss the signaling pathways involving extracellular cytokines and intracellular transmission, as well as the cross-talk between them. In the discussion, we also paid more attention to the potential metabolic and epigenetic mechanisms of psoriasis and the molecular mechanistic cascades related to its comorbidities. This review also outlined current treatment for psoriasis, especially targeted therapies and novel therapeutic strategies, as well as the potential mechanism of disease recurrence.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insights into interplay of immunopathophysiological events and molecular mechanistic cascades in psoriasis and its associated comorbidities.J Autoimmun. 2021 Mar;118:102614. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102614. Epub 2021 Feb 9. J Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33578119 Review.
-
The Inflammatory Response in Psoriasis: a Comprehensive Review.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016 Jun;50(3):377-89. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8535-x. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27025861 Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms and Management of a Cutaneous Inflammatory Disorder: Psoriasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 11;18(12):2684. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122684. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29232931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune cells in the epithelial immune microenvironment of psoriasis: emerging therapeutic targets.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 4;14:1340677. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1340677. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38239345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psoriasis: Recent progress in molecular-targeted therapies.J Dermatol. 2021 Jun;48(6):761-777. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15727. Epub 2021 Jan 6. J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33404109 Review.
Cited by
-
The Expression of Cytokines and Chemokines Potentially Distinguishes Mild and Severe Psoriatic Non-Lesional and Resolved Skin from Healthy Skin and Indicates Different Stages of Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 20;25(20):11292. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011292. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457071 Free PMC article.
-
Botulinum Toxin Treatment of Psoriasis-A Comprehensive Review.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Oct 18;16(10):449. doi: 10.3390/toxins16100449. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39453225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sprayable inflammasome-inhibiting lipid nanorods in a polymeric scaffold for psoriasis therapy.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 19;15(1):9035. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53396-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39426974 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the psoriasis research landscape: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis from 2012-2023.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Dec;38:3946320241290341. doi: 10.1177/03946320241290341. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39393083 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Advances in Psoriasis: From Biologics to Emerging Oral Small Molecules.Antibodies (Basel). 2024 Sep 14;13(3):76. doi: 10.3390/antib13030076. Antibodies (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39311381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

