Determination of Gastric Water Emptying in Fasted and Fed State Conditions Using a Compression-Coated Tablet and Salivary Caffeine Kinetics
- PMID: 38004563
- PMCID: PMC10674960
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112584
Determination of Gastric Water Emptying in Fasted and Fed State Conditions Using a Compression-Coated Tablet and Salivary Caffeine Kinetics
Abstract
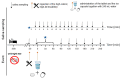
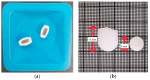
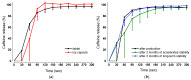
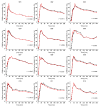
Because of the importance of gastric emptying for pharmacokinetics, numerous methods have been developed for its determination. One of the methods is the salivary tracer technique, which utilizes an ice capsule containing caffeine as a salivary tracer. Despite the ice capsule's advantage in labeling ingested fluids with caffeine for subsequent salivary detection, its risk of premature melting before swallowing, and its complicated storage and preparation, limit its application, particularly in special populations (e.g., older people). For this reason, here, a compression-coated tablet was developed and validated against the ice capsule in a cross-over clinical trial. The two dosage forms were administered simultaneously to 12 volunteers in an upright position under fasted and fed state conditions. To distinguish the caffeine concentrations in saliva from each dosage form, regular type of caffeine (12C) was added to the tablet, while for the ice capsule 13C3 labelled caffeine was used. The salivary caffeine concentrations showed no statistically significant differences for the pharmacokinetic parameters tmax and AUC0→60 (p > 0.05). Thus, the new formulation is a useful tool for determining gastric emptying that can also be used in special populations.
Keywords: caffeine; compression-coated tablet; fasted and fed state conditions; gastric emptying; in vivo study; salivary tracer technique.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
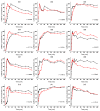
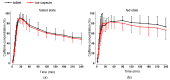
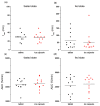
Similar articles
-
Low dose caffeine as a salivary tracer for the determination of gastric water emptying in fed and fasted state: A MRI validation study.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018 Jun;127:443-452. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.03.011. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018. PMID: 29602018
-
Impact of advanced age on the gastric emptying of water under fasted and fed state conditions.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2024 Oct 1;201:106853. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2024.106853. Epub 2024 Jul 20. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39033883
-
Comparing Salivary Caffeine Kinetics of 13C and 12C Caffeine for Gastric Emptying of 50 mL Water.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 18;15(2):328. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020328. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839650 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo characterization of enTRinsic™ drug delivery technology capsule after intake in fed state: A cross-validation approach using salivary tracer technique in comparison to MRI.J Control Release. 2019 Nov 10;313:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.10.023. Epub 2019 Oct 15. J Control Release. 2019. PMID: 31626859 Clinical Trial.
-
Combined Application of MRI and the Salivary Tracer Technique to Determine the in Vivo Disintegration Time of Immediate Release Formulation Administered to Healthy, Fasted Subjects.Mol Pharm. 2019 Apr 1;16(4):1782-1786. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b01320. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Mol Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30821987
References
-
- Stillhart C., Vučićević K., Augustijns P., Basit A.W., Batchelor H., Flanagan T.R., Gesquiere I., Greupink R., Keszthelyi D., Koskinen M., et al. Impact of Gastrointestinal Physiology on Drug Absorption in Special Populations––An UNGAP Review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020;147:105280. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105280. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

