Circulating Extracellular Vesicle-Derived microRNAs as Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Non-Viral-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 38003232
- PMCID: PMC10671272
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216043
Circulating Extracellular Vesicle-Derived microRNAs as Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Non-Viral-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
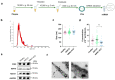
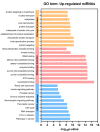
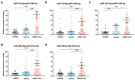
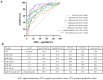
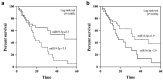
Extracellular vesicle-derived microRNAs (EV-miRNAs) are promising circulating biomarkers for chronic liver disease. In this study, we explored the potential significance of plasma EV-miRNAs in non-hepatitis B-, non-hepatitis C-related HCC (NBNC-HCC). We compared, using the NanoString method, plasma EV-miRNA profiles between NBNC-HCC and control groups including patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and healthy controls. The differentially expressed EV-miRNAs were validated in another set of plasma samples by qRT-PCR. A total of 66 significantly differentially expressed EV-miRNAs between the HCC and the control groups were identified in the discovery set. In the validation cohort, including plasma samples of 70 NBNC-HCC patients, 70 NAFLD patients, and 35 healthy controls, 5 plasma EV-miRNAs were significantly elevated in HCC, which included miR-19-3p, miR-16-5p, miR-223-3p, miR-30d-5p, and miR-451a. These miRNAs were found to participate in several cancer-related signaling pathways based on bioinformatic analysis. Among them, EV-miR-19-3p exhibited the best diagnostic performance and displayed a high sensitivity for detecting alpha-fetoprotein-negative HCC and early-stage HCC. In multivariate analysis, a high EV-miR-19-3p level was demonstrated as an independently unfavorable predictor of overall survival in patients with NBNC-HCC. In conclusion, our data have indicated, for the first time, that EV-miR-19-3p could serve as a novel circulating biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of NBNC-HCC.
Keywords: biomarker; extracellular vesicles; hepatocellular carcinoma; microRNAs; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic and prognostic roles of circulating miRNA-223-3p in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 24;15(4):e0232211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232211. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32330203 Free PMC article.
-
The exosome encapsulated microRNAs as circulating diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma with low alpha-fetoprotein.Int J Cancer. 2020 Nov 15;147(10):2934-2947. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33111. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32441313
-
Profiles of serum microRNAs; miR-125b-5p and miR223-3p serve as novel biomarkers for HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Jul;41(7):4513-9. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3322-3. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24595450
-
Identification of circulating MicroRNAs as novel potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma detection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2015 Sep;17(9):684-93. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1294-y. Epub 2015 May 9. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25956842 Review.
-
MicroRNAs as possible biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatitis B- and C-related-hepatocellular-carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Apr 21;22(15):3907-36. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i15.3907. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27099435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles and cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma - is there a link?Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 27;15:1368898. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1368898. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38476233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 24;10(17):e36890. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36890. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281542 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles in hepatocellular carcinoma: unraveling immunological mechanisms for enhanced diagnosis and overcoming drug resistance.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 28;15:1485628. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485628. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39530097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Circulating microRNAs in Liver Disease and HCC: Focus on miR-122.Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;15(10):1313. doi: 10.3390/genes15101313. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Related Non-Coding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Overview.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 4;16(7):1415. doi: 10.3390/cancers16071415. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li J., Zou B., Yeo Y.H., Feng Y., Xie X., Lee D.H., Fujii H., Wu Y., Kam L.Y., Ji F., et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999–2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019;4:389–398. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30039-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hsu P.Y., Hsu C.T., Yeh M.L., Huang C.F., Huang C.I., Liang P.C., Lin Y.H., Hsieh M.Y., Wei Y.J., Hsieh M.H., et al. Early Fibrosis but Late Tumor Stage and Worse Outcomes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Without Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020;65:2120–2129. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05938-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Toyoda H., Kariyama K., Hiraoka A., Tsuji K., Ishikawa T., Hatanaka T., Naganuma A., Yasuda S., Nouso K., Kakizaki S., et al. Improved survival of viral hepatocellular carcinoma but not non-viral hepatocellular carcinoma from 2000 to 2020: A multi-centre cohort study of 6007 patients from high-volume academic centres in Japan. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022;56:694–701. doi: 10.1111/apt.17088. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N41A640187/National Research Council of Thailand
- Second Century Fund (C2F)
- Program Management Unit for Human Resources & Institutional Development, Research and Innovation (PMU-B)
- Center of Excellence in Hepatitis and Liver Cancer, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University
- CUFRB65_hea(14)_021_30_02/Fundamental Fund 2022, Thailand Science Research and Innovation (TSRI) via Chulalongkorn University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

