Data Mining Suggests That CXCL14 Gene Silencing in Colon Cancer Is Due to Promoter Methylation
- PMID: 38003215
- PMCID: PMC10671198
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242216027
Data Mining Suggests That CXCL14 Gene Silencing in Colon Cancer Is Due to Promoter Methylation
Abstract
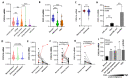
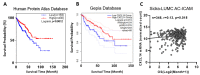
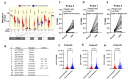
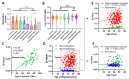
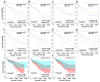
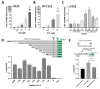
CXCL14 is one of the most evolutionarily conserved members of the chemokine family and is constitutionally expressed in multiple organs, suggesting that it is involved in the homeostasis maintenance of the system. CXCL14 is highly expressed in colon epithelial cells and shows obvious gene silencing in clinical colon cancer samples, suggesting that its silencing is related to the immune escape of cancer cells. In this paper, we analyzed the expression profiles of multiple human clinical colon cancer datasets and mouse colon cancer models to reveal the variation trend of CXCL14 expression during colitis, colon polyps, primary colon cancer, and liver metastases. The relationship between CXCL14 gene silencing and promoter hypermethylation was revealed through the colorectal carcinoma methylation database. The results suggest that CXCL14 is a tumor suppressor gene in colorectal carcinoma which is activated first and then silenced during the process of tumor occurrence and deterioration. Promoter hypermethylation is the main cause of CXCL14 silencing. The methylation level of CXCL14 is correlated with the anatomic site of tumor occurrence, positively correlated with patient age, and associated with prognosis. Reversing the hypermethylation of CXCL14 may be an epigenetic therapy for colon cancer.
Keywords: CXCL14; DNA methylation; colorectal cancer; gene silence; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic silencing of CXCL14 induced colorectal cancer migration and invasion.Discov Med. 2013 Oct;16(88):137-47. Discov Med. 2013. PMID: 24099668 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal hypermethylation of promoter region downregulates chemokine CXC ligand 14 expression in gastric cancer.Int J Oncol. 2013 Nov;43(5):1487-94. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2078. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23982764
-
Expression and effect of CXCL14 in colorectal carcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Sep;10(3):1561-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2343. Epub 2014 Jun 17. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24938992
-
The multifarious roles of the chemokine CXCL14 in cancer progression and immune responses.Mol Carcinog. 2020 Jul;59(7):794-806. doi: 10.1002/mc.23188. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Mol Carcinog. 2020. PMID: 32212206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokine CXCL14; a double-edged sword in cancer development.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Aug;97:107681. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107681. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33932697 Review.
Cited by
-
CXCL14 as a Key Regulator of Neuronal Development: Insights from Its Receptor and Multi-Omics Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 29;25(3):1651. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031651. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338930 Free PMC article.
-
Insights of Expression Profile of Chemokine Family in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 9;25(19):10857. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910857. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409185 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic reprogramming in gastrointestinal cancer: biology and translational perspectives.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 24;5(9):e670. doi: 10.1002/mco2.670. eCollection 2024 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39184862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and prognostic analysis of candidate biomarkers for lung metastasis in colorectal cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Mar 15;103(11):e37484. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037484. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38489730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shellenberger T.D., Wang M., Gujrati M., Jayakumar A., Strieter R.M., Burdick M.D., Ioannides C.G., Efferson C.L., El-Naggar A.K., Roberts D., et al. BRAK/CXCL14 is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis and a chemotactic factor for immature dendritic cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:8262–8270. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2056. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32171246/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32200531/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21JC1403700/Shanghai Municipal Government Science Innovation grant
- YG2022QN114/Joint Research Funds for Medical and Engineering and Scientific Research at Shanghai Jiao Tong University
- YG2022QN082/Joint Research Funds for Medical and Engineering and Scientific Research at Shanghai Jiao Tong University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

