Navigating the Gene Co-Expression Network and Drug Repurposing Opportunities for Brain Disorders Associated with Neurocognitive Impairment
- PMID: 38002524
- PMCID: PMC10669457
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13111564
Navigating the Gene Co-Expression Network and Drug Repurposing Opportunities for Brain Disorders Associated with Neurocognitive Impairment
Abstract
Neurocognitive impairment refers to a spectrum of disorders characterized by a decline in cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving, which are often linked to structural or functional abnormalities in the brain. While its exact etiology remains elusive, genetic factors play a pivotal role in disease onset and progression. This study aimed to identify highly correlated gene clusters (modules) and key hub genes shared across neurocognition-impairing diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease with dementia (PDD), HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND), and glioma. Herein, the microarray datasets AD (GSE5281), HAND (GSE35864), glioma (GSE15824), and PD (GSE7621) were used to perform Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) to identify highly preserved modules across the studied brain diseases. Through gene set enrichment analysis, the shared modules were found to point towards processes including neuronal transcriptional dysregulation, neuroinflammation, protein aggregation, and mitochondrial dysfunction, hallmarks of many neurocognitive disorders. These modules were used in constructing protein-protein interaction networks to identify hub genes shared across the diseases of interest. These hub genes were found to play pivotal roles in processes including protein homeostasis, cell cycle regulation, energy metabolism, and signaling, all associated with brain and CNS diseases, and were explored for their drug repurposing experiments. Drug repurposing based on gene signatures highlighted drugs including Dorzolamide and Oxybuprocaine, which were found to modulate the expression of the hub genes in play and may have therapeutic implications in neurocognitive disorders. While both drugs have traditionally been used for other medical purposes, our study underscores the potential of a combined WGCNA and drug repurposing strategy for searching for new avenues in the simultaneous treatment of different diseases that have similarities in gene co-expression networks.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; WGCNA; drug repurposing; hub genes; microarray; neurocognitive disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


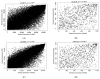


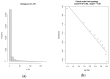
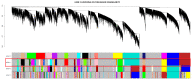

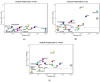

Similar articles
-
Systems analysis of human brain gene expression: mechanisms for HIV-associated neurocognitive impairment and common pathways with Alzheimer's disease.BMC Med Genomics. 2013 Feb 13;6:4. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-6-4. BMC Med Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23406646 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering neuroinflammation-related modules and potential repurposing drugs for Alzheimer's disease through multi-omics data integrative analysis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Jun 2;15:1161405. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1161405. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37333458 Free PMC article.
-
[Identification of potential hub genes of Alzheimer's disease by weighted gene co-expression network analysis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 Dec 20;41(12):1752-1762. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.12.01. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 35012905 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Plasma neuronal exosomes serve as biomarkers of cognitive impairment in HIV infection and Alzheimer's disease.J Neurovirol. 2019 Oct;25(5):702-709. doi: 10.1007/s13365-018-0695-4. Epub 2019 Jan 4. J Neurovirol. 2019. PMID: 30610738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Hub Genes Reveals Associated Inflammatory Pathways in Estrogen-Dependent Gynecological Diseases.Biology (Basel). 2024 May 30;13(6):397. doi: 10.3390/biology13060397. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927277 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Modular Hub Genes and Therapeutic Targets across Stages of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Transcriptome.Genes (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;15(10):1248. doi: 10.3390/genes15101248. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457373 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical Studies of DNA Microarray Present Potential Molecular and Cellular Interconnectivity of Signaling Pathways in Immune System Dysregulation.Genes (Basel). 2024 Mar 22;15(4):393. doi: 10.3390/genes15040393. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674328 Free PMC article.
-
Modular Hub Genes in DNA Microarray Suggest Potential Signaling Pathway Interconnectivity in Various Glioma Grades.Biology (Basel). 2024 Mar 23;13(4):206. doi: 10.3390/biology13040206. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38666818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grethlein D., Kandadai V., Dampier W. Classification of Drivers with HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders using Virtual Driving Test Performance Data; Proceedings of the International FLAIRS Conference Proceedings; Clearwater Beach, FL, USA. 14–17 May 2023; - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

