Carfilzomib Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide/D-Galactosamine/Dimethylsulfoxide-Induced Acute Liver Failure in Mice
- PMID: 38002097
- PMCID: PMC10669466
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11113098
Carfilzomib Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide/D-Galactosamine/Dimethylsulfoxide-Induced Acute Liver Failure in Mice
Abstract
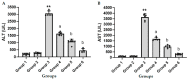
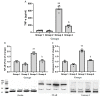
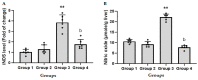
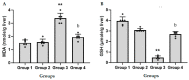
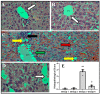
Acute liver failure (ALF) is a disease accompanied by severe liver inflammation. No effective therapy is available yet apart from liver transplantation; therefore, developing novel treatments for ALF is urgently required. Inflammatory mediators released by NF-кB activation play an essential role in ALF. Proteasome inhibitors have many medical uses, such as reducing inflammation and NF-кB inhibition, which are believed to account for most of their repurposing effects. This study was undertaken to explore the possible protective effects and the underlying mechanisms of carfilzomib, a proteasome inhibitor, in a mouse model of ALF induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine/dimethylsulfoxide (LPS/GalN/DMSO). Carfilzomib dose-dependently protected mice from LPS/GalN/DMSO-induced liver injury, as indicated by the decrease in serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels. LPS/GalN/DMSO increased TNF-α, NF-кB, lipid peroxidation, NO, iNOS, cyclooxygenase-II, myeloperoxidase, and caspase-3 levels. Carfilzomib administration mitigated LPS/GalN/DMSO-induced liver damage by decreasing the elevated levels of TNF-α, NF-кB, lipid peroxidation, nitric oxide, iNOS, cyclooxygenase-II, myeloperoxidase, caspase-3, and histopathological changes. A restored glutathione level was also observed in the carfilzomib-treated LPS/GalN/DMSO mice. Our results demonstrate that carfilzomib protects against LPS/GalN/DMSO-induced ALF by inhibiting NF-кB, decreasing inflammatory mediators, oxidative/nitrosative stress, neutrophil recruitment, and apoptosis, suggesting that carfilzomib may be a potential therapeutic agent for ALF.
Keywords: animal model; carfilzomib; hepatotoxicity; inflammation; oxidative and nitrosative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective Role of 4-Octyl Itaconate in Murine LPS/D-GalN-Induced Acute Liver Failure via Inhibiting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Aug 17;2021:9932099. doi: 10.1155/2021/9932099. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34457120 Free PMC article.
-
Role of α-lipoic acid in LPS/d-GalN induced fulminant hepatic failure in mice: studies on oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Oct;22(2):293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.07.008. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25046589
-
Salvage effect of E5564, Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist on d-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure in rats.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 May;25(5):1009-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06145.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20546456
-
UMSCs Attenuate LPS/D-GalN-induced Acute Liver Failure in Mice by Down-regulating the MyD88/NF-κB Pathway.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021 Oct 28;9(5):690-701. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00157. Epub 2021 Apr 22. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34722184 Free PMC article.
-
Daphnetin alleviates lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure via the inhibition of NLRP3, MAPK and NF-κB, and the induction of autophagy.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Nov;119:240-248. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.07.101. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 30031824
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

