Self-Cleavage of Human Chloride Channel Accessory 2 Causes a Conformational Shift That Depends on Membrane Anchorage and Is Required for Its Regulation of Store-Operated Calcium Entry
- PMID: 38001916
- PMCID: PMC10669480
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11112915
Self-Cleavage of Human Chloride Channel Accessory 2 Causes a Conformational Shift That Depends on Membrane Anchorage and Is Required for Its Regulation of Store-Operated Calcium Entry
Abstract
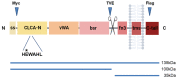
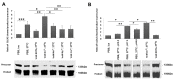
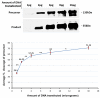
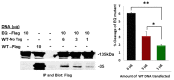
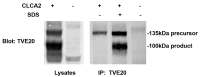
Human CLCA2 regulates store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) by interacting with Orai1 and STIM1. It is expressed as a 943aa type I transmembrane protein that is cleaved at amino acid 708 to produce a diffusible 100 kDa product. The N-terminal ectodomain contains a hydrolase-like subdomain with a conserved HEXXH zinc-binding motif that is proposed to cleave the precursor autoproteolytically. Here, we tested this hypothesis and its link to SOCE. We first studied the conditions for autocleavage in isolated membranes and then in a purified protein system. Cleavage was zinc-dependent and abolished by mutation of the E in the HEXXH motif to Q, E165Q. Cleavage efficiency increased with CLCA2 concentration, implying that it occurs in trans. Accordingly, the E165Q mutant was cleaved by co-transfected wildtype CLCA2. Moreover, CLCA2 precursors with different epitope tags co-immunoprecipitated. In a membrane-free system utilizing immunopurified protease and target, no cleavage occurred unless the target was first denatured, implying that membranes provide essential structural or conformational cues. Unexpectedly, cleavage caused a conformational shift: an N-terminal antibody that immunoprecipitated the precursor failed to precipitate the N-terminal product unless the product was first denatured with an ionic detergent. The E165Q mutation abolished the stimulation of SOCE caused by wildtype CLCA2, establishing that the metalloprotease activity is required for this regulatory function.
Keywords: CLCA2; SOCE; metalloprotease; self-cleavage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Store-Independent Orai Channels Regulated by STIM.In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 11. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 11. PMID: 30299650 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Regulation and Role of Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry in Cellular Proliferation.In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 12. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 12. PMID: 30299656 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
CLCA2 is a positive regulator of store-operated calcium entry and TMEM16A.PLoS One. 2018 May 14;13(5):e0196512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196512. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29758025 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Orai1 and STIM1 by Cellular Factors.In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 4. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 4. PMID: 30299655 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Differential dependence of store-operated and excitation-coupled Ca2+ entry in skeletal muscle on STIM1 and Orai1.J Physiol. 2008 Oct 15;586(20):4815-24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.160481. Epub 2008 Sep 4. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18772199 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walia V., Yu Y., Cao D., Sun M., McLean J.R., Hollier B.G., Cheng J., Mani S.A., Rao K., Premkumar L., et al. Loss of breast epithelial marker hCLCA2 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and indicates higher risk of metastasis. Oncogene. 2012;31:2237–2246. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.392. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gruber A.D., Fuller C.M., Elble R.C., Benos D.J., Pauli B.U. The CLCA Gene Family A Novel Family of Putative Chloride Channels. Curr. Genom. 2000;1:201–222. doi: 10.2174/1389202003351526. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

