Mfn2 regulates mitochondria-associated ER membranes to affect PCOS oocyte development
- PMID: 37988456
- PMCID: PMC10762585
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-23-0343
Mfn2 regulates mitochondria-associated ER membranes to affect PCOS oocyte development
Abstract
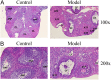
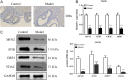
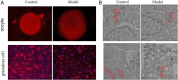
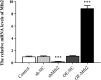
This study aimed to investigate the role of mitochondrial-related protein Mfn2 in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and its impact on oocyte development. The pathological features of PCOS model mice were confirmed by hematoxylin-eosin staining and immunohistochemistry. The expression of Mfn2 and mitochondrial-related proteins in PCOS oocytes and granulosa cells was detected by qRT-PCR and Western blot. Mitochondrial quantity was measured by Mito-Tracker staining, and the structure of mitochondria-associated ER membranes (MAMs) was observed by transmission electron microscopy. The results showed that Mfn2 was significantly downregulated in PCOS oocytes and granulosa cells, and its expression was inhibited in oocytes at different developmental stages. Moreover, the structure of MAMs was also disrupted. Downregulation of Mfn2 expression led to a reduction in mitochondrial quantity in oocytes and granulosa cells, as well as disruption of MAM structure, while overexpression of Mfn2 had the opposite effect. In conclusion, this study indicates that Mfn2 affects the development of PCOS oocytes by regulating MAMs and may be involved in maintaining the stability of MAM structure and function, thereby affecting mitochondrial quantity and function. These findings provide new insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of PCOS.
Keywords: Mfn2; mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes; oocyte granulosa cells; polycystic ovary syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the study reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial redox-driven mitofusin 2 S-glutathionylation promotes neuronal necroptosis via disrupting ER-mitochondria crosstalk in cadmium-induced neurotoxicity.Chemosphere. 2021 Jan;262:127878. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127878. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Chemosphere. 2021. PMID: 33182097
-
Mfn2 Regulates High Glucose-Induced MAMs Dysfunction and Apoptosis in Podocytes via PERK Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 20;9:769213. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.769213. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34988075 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of MFN2 alleviates sorafenib-induced cardiomyocyte necroptosis via the MAM-CaMKIIδ pathway in vitro and in vivo.Theranostics. 2022 Jan 1;12(3):1267-1285. doi: 10.7150/thno.65716. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35154486 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane proteins in diseases.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 May;199:115011. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115011. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35314166 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in PCOS: Insights into Reproductive Organ Pathophysiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 23;24(17):13123. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713123. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37685928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GRB7-mediated enhancement of cell malignant characteristics induced by Helicobacter pylori infection.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 18;15:1469953. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1469953. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39360313 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

