When Autoantibodies Are Missing: The Challenge of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 37987247
- PMCID: PMC10660552
- DOI: 10.3390/antib12040069
When Autoantibodies Are Missing: The Challenge of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
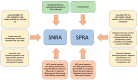
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (SNRA) is characterized by the absence of both rheumatoid factor (RF) and antibodies against the cyclic citrullinated protein (ACPA) in serum. However, the differences between the two forms of RA are more complex and have not yet been definitively characterized. Several lines of evidences support the idea that there are specific elements of the two forms, including genetic background, epidemiology, pathogenesis, severity of progression over time, and response to therapy. Clinical features that may differentiate SNRA from SPRA are also suggested by data obtained from classical radiology and newer imaging techniques. Although new evidence seems to provide additional help in differentiating the two forms of RA, their distinguishing features remain largely elusive. It should also be emphasized that the distinctive features of RA forms, if not properly recognized, can lead to the underdiagnosis of SNRA, potentially missing the period called the "window of opportunity" that is critical for early diagnosis, timely treatment, and better prognosis. This review aims to summarize the data provided in the scientific literature with the goal of helping clinicians diagnose SNRA as accurately as possible, with emphasis on the most recent findings available.
Keywords: anti-citrullinated protein antibodies; rheumatoid factor; seronegative rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differing X-ray patterns in seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2019 Sep;38(9):2403-2410. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04602-5. Epub 2019 May 23. Clin Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31123977
-
Clinical management of seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: A comparative study.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 6;13(4):e0195550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195550. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29624625 Free PMC article.
-
Differential immunological profiles in seronegative versus seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: Th17/Treg dysregulation and IL-4.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 3;15:1447213. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447213. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39290695 Free PMC article.
-
Is ACPA positivity the main driver for rheumatoid arthritis treatment? Pros and cons.Autoimmun Rev. 2017 Nov;16(11):1096-1102. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Autoimmun Rev. 2017. PMID: 28899798 Review.
-
Autoantibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Historical Background and Novel Findings.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2022 Oct;63(2):138-151. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08890-1. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34495490 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Phenotypes, Serological Biomarkers, and Synovial Features Defining Seropositive and Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Literature Review.Cells. 2024 Apr 24;13(9):743. doi: 10.3390/cells13090743. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38727279 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aletaha D., Neogi T., Silman A.J., Funovits J., Felson D.T., Bingham C.O., 3rd, Birnbaum N.S., Burmester G.R., Bykerk V.P., Cohen M.D., et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–2581. doi: 10.1002/art.27584. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

