This is a preprint.
Systematic Dissection of Sequence Features Affecting the Binding Specificity of a Pioneer Factor Reveals Binding Synergy Between FOXA1 and AP-1
- PMID: 37986839
- PMCID: PMC10659273
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.08.566246
Systematic Dissection of Sequence Features Affecting the Binding Specificity of a Pioneer Factor Reveals Binding Synergy Between FOXA1 and AP-1
Update in
-
Systematic dissection of sequence features affecting binding specificity of a pioneer factor reveals binding synergy between FOXA1 and AP-1.Mol Cell. 2024 Aug 8;84(15):2838-2855.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.06.022. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39019045
Abstract
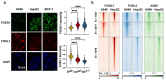
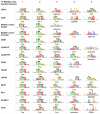
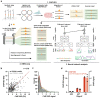
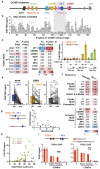
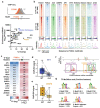
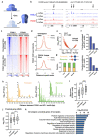
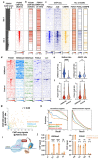
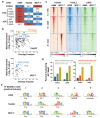
Despite the unique ability of pioneer transcription factors (PFs) to target nucleosomal sites in closed chromatin, they only bind a small fraction of their genomic motifs. The underlying mechanism of this selectivity is not well understood. Here, we design a high-throughput assay called ChIP-ISO to systematically dissect sequence features affecting the binding specificity of a classic PF, FOXA1. Combining ChIP-ISO with in vitro and neural network analyses, we find that 1) FOXA1 binding is strongly affected by co-binding TFs AP-1 and CEBPB, 2) FOXA1 and AP-1 show binding cooperativity in vitro, 3) FOXA1's binding is determined more by local sequences than chromatin context, including eu-/heterochromatin, and 4) AP-1 is partially responsible for differential binding of FOXA1 in different cell types. Our study presents a framework for elucidating genetic rules underlying PF binding specificity and reveals a mechanism for context-specific regulation of its binding.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Systematic dissection of sequence features affecting binding specificity of a pioneer factor reveals binding synergy between FOXA1 and AP-1.Mol Cell. 2024 Aug 8;84(15):2838-2855.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.06.022. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39019045
-
A test of the pioneer factor hypothesis using ectopic liver gene activation.Elife. 2022 Jan 5;11:e73358. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73358. Elife. 2022. PMID: 34984978 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis reveals positional-nucleosome-oriented binding pattern of pioneer factor FOXA1.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 19;44(16):7540-54. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw659. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27458208 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of pioneer transcription factors in targeted ERα positive breast cancer.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2021;2(1):26-35. doi: 10.37349/etat.2021.00031. Epub 2021 Feb 28. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2021. PMID: 36046086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pioneer factors and ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling factors interact dynamically: A new perspective: Multiple transcription factors can effect chromatin pioneer functions through dynamic interactions with ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling factors.Bioessays. 2016 Nov;38(11):1150-1157. doi: 10.1002/bies.201600137. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 27633730 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Spitz F. & Furlong E.E. Transcription factors: from enhancer binding to developmental control. Nat Rev Genet 13, 613–26 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
