Optimisation of Non-Pharmaceutical Measures in COVID-19 Growth via Neural Networks
- PMID: 37982015
- PMCID: PMC8769028
- DOI: 10.1109/TETCI.2020.3046012
Optimisation of Non-Pharmaceutical Measures in COVID-19 Growth via Neural Networks
Abstract
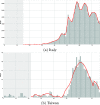
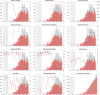
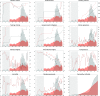
On [Formula: see text] March, the World Health Organisation declared a pandemic. Through this global spread, many nations have witnessed exponential growth of confirmed cases brought under control by severe mass quarantine or lockdown measures. However, some have, through a different timeline of actions, prevented this exponential growth. Currently as some continue to tackle growth, others attempt to safely lift restrictions whilst avoiding a resurgence. This study seeks to quantify the impact of government actions in mitigating viral transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by a novel soft computing approach that makes concurrent use of a neural network model, to predict the daily slope increase of cumulative infected, and an optimiser, with a parametrisation of the government restriction time series, to understand the best set of mitigating actions. Data for two territories, Italy and Taiwan, have been gathered to model government restrictions in travelling, testing and enforcement of social distance measures as well as people connectivity and adherence to government actions. It is found that a larger and earlier testing campaign with tighter entry restrictions benefit both regions, resulting in significantly less confirmed cases. Interestingly, this scenario couples with an earlier but milder implementation of nationwide restrictions for Italy, thus supporting Taiwan's lack of nationwide lockdown, i.e. earlier government actions could have contained the growth to a degree that a widespread lockdown would have been avoided, or at least delayed. The results, found with a purely data-driven approach, are in line with the main findings of mathematical epidemiological models, proving that the proposed approach has value and that the data alone contains valuable knowledge to inform decision makers.
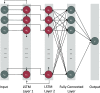
Keywords: BiLSTM; CNN; Covid-19; ELM; SARS-CoV-2; data gathering; epidemiology; optimisation.
© IEEE 2021.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID-19: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013574. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013574.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33959956 Free PMC article.
-
Could masks curtail the post-lockdown resurgence of COVID-19 in the US?Math Biosci. 2020 Nov;329:108452. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2020.108452. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Math Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32818515 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 30;1(1):CD006207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006207.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36715243 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of artificial intelligence in battling against covid-19: A literature review.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021 Jan;142:110338. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110338. Epub 2020 Oct 3. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021. PMID: 33041533 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- W. H. Organization, “Novel coronavirus (2019-ncov): Situation report, 1,” , 2020-01-21.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
