Association of biomarkers of enteric dysfunction, systemic inflammation, and growth hormone resistance with seroconversion to oral rotavirus vaccine: A lasso for inference approach
- PMID: 37976323
- PMCID: PMC10656027
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293101
Association of biomarkers of enteric dysfunction, systemic inflammation, and growth hormone resistance with seroconversion to oral rotavirus vaccine: A lasso for inference approach
Abstract
Background: Rotavirus gastroenteritis remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality despite the introduction of vaccines. Research shows there are several factors contributing to the reduced efficacy of rotavirus vaccines in low- and middle-income settings. Proposed factors include environmental enteric dysfunction (EED), malnutrition, and immune dysfunction. This study aimed to assess the effect of these factors on vaccine responses using a machine learning lasso approach.
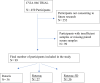
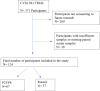
Methods: Serum samples from two rotavirus clinical trials (CVIA 066 n = 99 and CVIA 061 n = 124) were assessed for 11 analytes using the novel Micronutrient and EED Assessment Tool (MEEDAT) multiplex ELISA. Immune responses to oral rotavirus vaccines (Rotarix, Rotavac, and Rotavac 5D) as well as a parenteral rotavirus vaccine (trivalent P2-VP8) were also measured and machine learning using the lasso approach was then applied to investigate any associations between immune responses and environmental enteric dysfunction, systemic inflammation, and growth hormone resistance biomarkers.
Results: Both oral and parenteral rotavirus vaccine responses were negatively associated with retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4), albeit only weakly for oral vaccines. The parenteral vaccine responses were positively associated with thyroglobulin (Tg) and histidine-rich protein 2 (HRP2) for all three serotypes (P8, P6 and P4), whilst intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP) was negatively associated with P6 and P4, but not P8, and soluble transferrin receptor (sTfR) was positively associated with P6 only.
Conclusion: MEEDAT successfully measured biomarkers of growth, systemic inflammation, and EED in infants undergoing vaccination, with RBP4 being the only analyte associated with both oral and parenteral rotavirus vaccine responses. Tg and HRP2 were associated with responses to all three serotypes in the parenteral vaccine, while I-FABP and sTfR results indicated possible strain specific immune responses to parenteral immunization.
Copyright: © 2023 Mwila-Kazimbaya et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8(8):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32851663 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for supporting pregnant women's decision-making about mode of birth after a caesarean.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 30;2013(7):CD010041. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010041.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23897547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-rich therapies for musculoskeletal soft tissue injuries.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):CD010071. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010071.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24782334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO. Rotavirus Vaccines WHO Position Paper- January 2013. Weekly Epidemiological Report. 2013;88: 49–64. Available: http://www.who.int/wer/2013/wer8805/en/#.V9_gYyZkESI.mendeley
-
- Mwila-Kazimbaya K, Bosomprah S, Simuyandi M, Chisenga CC, Munsaka S. Efficacy and Effectiveness of Rotavirus Vaccine on Incidence of Diarrhoea among. Pediatr Infect Dis. 2018;3: 1–11. doi: 10.4172/2573-0282.100060 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous