The molecular landscape of neurological disorders: insights from single-cell RNA sequencing in neurology and neurosurgery
- PMID: 37974227
- PMCID: PMC10652629
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-023-01504-w
The molecular landscape of neurological disorders: insights from single-cell RNA sequencing in neurology and neurosurgery
Abstract
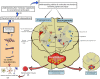
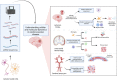
Single-cell ribonucleic acid sequencing (scRNA-seq) has emerged as a transformative technology in neurological and neurosurgical research, revolutionising our comprehension of complex neurological disorders. In brain tumours, scRNA-seq has provided valuable insights into cancer heterogeneity, the tumour microenvironment, treatment resistance, and invasion patterns. It has also elucidated the brain tri-lineage cancer hierarchy and addressed limitations of current models. Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis have been molecularly subtyped, dysregulated pathways have been identified, and potential therapeutic targets have been revealed using scRNA-seq. In epilepsy, scRNA-seq has explored the cellular and molecular heterogeneity underlying the condition, uncovering unique glial subpopulations and dysregulation of the immune system. ScRNA-seq has characterised distinct cellular constituents and responses to spinal cord injury in spinal cord diseases, as well as provided molecular signatures of various cell types and identified interactions involved in vascular remodelling. Furthermore, scRNA-seq has shed light on the molecular complexities of cerebrovascular diseases, such as stroke, providing insights into specific genes, cell-specific expression patterns, and potential therapeutic interventions. This review highlights the potential of scRNA-seq in guiding precision medicine approaches, identifying clinical biomarkers, and facilitating therapeutic discovery. However, challenges related to data analysis, standardisation, sample acquisition, scalability, and cost-effectiveness need to be addressed. Despite these challenges, scRNA-seq has the potential to transform clinical practice in neurological and neurosurgical research by providing personalised insights and improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: Brain tumours; Cerebrovascular diseases; Epilepsy and seizure disorders; Neurodegenerative disorders; Neurology; Neurosurgery; Single-cell RNA sequencing; Spinal cord diseases.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring the current landscape of single-cell RNA sequencing applications in gastric cancer research.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(7):e18159. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18159. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38494861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the advances of single-cell RNA sequencing in thyroid cancer: a narrative review.Med Oncol. 2023 Dec 21;41(1):27. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02260-x. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38129369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing in breast cancer: Understanding tumor heterogeneity and paving roads to individualized therapy.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020 Aug;40(8):329-344. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12078. Epub 2020 Jul 12. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32654419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive review on single-cell RNA sequencing: A new frontier in Alzheimer's disease research.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Sep;100:102454. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102454. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 39142391 Review.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing in exploring the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Jul;14(7):e1751. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1751. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38946005 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bibliometric and visual analysis of single-cell multiomics in neurodegenerative disease arrest studies.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 8;15:1450663. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1450663. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39440247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Das S, Pradhan U, Rai SN. Five years of gene networks modeling in single-cell RNA-sequencing studies: current approaches and outstanding challenges. Curr Bioinform. 2022;17(10):888–908. doi: 10.2174/1574893617666220823114108. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

