Proteomic approach towards identification of seminal fluid biomarkers from individuals with severe oligozoospermia, cryptozoospermia and non-obstructive azoospermia: a pilot study
- PMID: 37969768
- PMCID: PMC10643378
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-23-130
Proteomic approach towards identification of seminal fluid biomarkers from individuals with severe oligozoospermia, cryptozoospermia and non-obstructive azoospermia: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Infertility becomes a global problem that affects to the same extent females and males. As reasons of male infertility can differ among individuals, the accurate diagnostics is essential for effective treatment. The most problematic both in diagnostics and in treatment are disturbances of spermatogenesis. Seminal fluid is rich in proteins that potentially can serve as markers for male infertility and among them, markers of spermatogenesis which are highly desired.
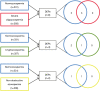
Methods: To find biomarkers of spermatogenesis, we applied comparative proteomics using nano ultra performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (nanoUPLC-MS/MS) followed by single-sample Western blotting (WB) using seminal fluid samples from males with different types of infertility including non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA), cryptozoospermia (C) and severe oligozoospermia (SO). Then, the extensive survey on the identified proteins and their function in male reproductive system has been done.
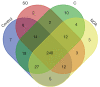
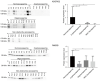
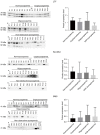
Results: The proteomic approach has enabled to identified five seminal fluid proteins being potential markers of spermatogenesis disorders: ADGRG2, RAB3B, LTF, SLC2A3 and spermine synthase (SMS). Among them ADGRG2 seems to be strongly involved in male infertility. In addition, WB indicated that the distribution of LTF, SLC2A3 and SMS was not coherent among the individuals, especially in a group with NOA. Functional annotation analysis and search in proteomics databases revealed that vast majority of the proteins originated from extracellular environment.
Conclusions: The presented data point out several proteins that potentially can become biomarkers of male infertility. The data suggest, however, different mechanisms behind the male infertility indicating that the etiology is more complex. We assume that recognition of these mechanisms may lead to the creation of specific protein panel helpful in the management of male infertility and therefore, further studies are required.
Keywords: Spermatogenesis; biomarkers; male infertility; pathological spermiogram; proteomics.
2023 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-23-130/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein markers of spermatogenesis and their potential use in the management of azoospermia.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021 Nov;18(11):939-948. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2021.2010548. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34812697
-
Evaluation of seminal plasma HSPA2 protein as a biomarker of human spermatogenesis status.Reprod Biol. 2022 Mar;22(1):100597. doi: 10.1016/j.repbio.2021.100597. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Reprod Biol. 2022. PMID: 34959194
-
Sequencing of a 'mouse azoospermia' gene panel in azoospermic men: identification of RNF212 and STAG3 mutations as novel genetic causes of meiotic arrest.Hum Reprod. 2019 Jun 4;34(6):978-988. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dez042. Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 31125047
-
Seminal Plasma Transcriptome and Proteome: Towards a Molecular Approach in the Diagnosis of Idiopathic Male Infertility.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 3;21(19):7308. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197308. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33022946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative Assessment of Seminal Plasma Biomarkers: A Narrative Review Bridging the Gap between Infertility Research and Clinical Practice.J Clin Med. 2024 May 27;13(11):3147. doi: 10.3390/jcm13113147. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38892858 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bringing proteomics to bear on male fertility: key lessons.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2024 Apr;21(4):181-203. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2024.2327553. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38536015 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
