Circulating serotonin and dopamine concentrations in osteoarthritis patients: a pilot study on the effect of pelotherapy
- PMID: 37962646
- PMCID: PMC10752847
- DOI: 10.1007/s00484-023-02571-8
Circulating serotonin and dopamine concentrations in osteoarthritis patients: a pilot study on the effect of pelotherapy
Abstract
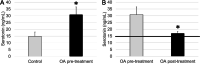
Balneotherapy has demonstrated clinical efficacy in the management of pathologies involving low-grade inflammation and stress. In rheumatic conditions such as osteoarthritis (OA), this therapy presents anti-inflammatory properties and potential to improve psychological well-being. Although the neurohormones serotonin and dopamine are known to be involved in these processes, surprisingly they have not been studied in this context. The objective was to evaluate the effect of a cycle of balneotherapy with peloids (pelotherapy) on circulating serotonin and dopamine concentrations in a group of aged individuals with OA, after comparing their basal state to that of an age-matched control group. In our pilot study, a pelotherapy program (10 days) was carried out in a group of 16 elderly patients with OA, evaluating its effects on circulating serotonin and dopamine concentrations (measured by ELISA). Individuals with OA showed higher levels of serotonin and lower dopamine levels, in line with the inflammatory roles of these mediators. After pelotherapy, serotonin concentrations significantly decreased, potentially contributing to the previously reported anti-inflammatory effects of balneotherapy.
Keywords: 5-HT; Hydrotherapy; Inflammation; Mud therapy; Pelotherapy; Spa therapy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spa therapy and peripheral serotonin and dopamine function: a systematic review.Int J Biometeorol. 2024 Jan;68(1):153-161. doi: 10.1007/s00484-023-02579-0. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Int J Biometeorol. 2024. PMID: 37950094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory effect as a mechanism of effectiveness underlying the clinical benefits of pelotherapy in osteoarthritis patients: regulation of the altered inflammatory and stress feedback response.Int J Biometeorol. 2017 Oct;61(10):1777-1785. doi: 10.1007/s00484-017-1361-x. Epub 2017 Apr 29. Int J Biometeorol. 2017. PMID: 28456879 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of mud-bath therapy on the innate/inflammatory responses in elderly patients with osteoarthritis: a discussion of recent results and a pilot study on the role of the innate function of monocytes.Int J Biometeorol. 2020 Jun;64(6):927-935. doi: 10.1007/s00484-019-01748-4. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Int J Biometeorol. 2020. PMID: 31218395
-
Innate/inflammatory bioregulation and clinical effectiveness of whole-body hyperthermia (balneotherapy) in elderly patients with osteoarthritis.Int J Hyperthermia. 2018;35(1):340-347. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1502896. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Int J Hyperthermia. 2018. PMID: 30295126
-
Balneotherapy (or spa therapy) for rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 11;2015(4):CD000518. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000518.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25862243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, Bole G, Borenstein D, Brandt K, Christy W, Cooke TD, Greenwald R, Hochberg M, et al. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986;29(8):1039–1049. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290816. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

