This is a preprint.
Legionella pneumophila exploits the endo-lysosomal network for phagosome biogenesis by co-opting SUMOylated Rab7
- PMID: 37961430
- PMCID: PMC10634985
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.10.31.564884
Legionella pneumophila exploits the endo-lysosomal network for phagosome biogenesis by co-opting SUMOylated Rab7
Update in
-
Legionella pneumophila exploits the endo-lysosomal network for phagosome biogenesis by co-opting SUMOylated Rab7.PLoS Pathog. 2024 May 13;20(5):e1011783. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011783. eCollection 2024 May. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38739652 Free PMC article.
Abstract
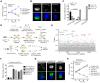
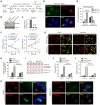
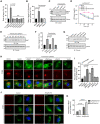
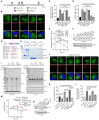
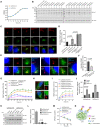
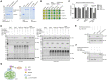
L. pneumophila strains harboring wild-type rpsL such as Lp02rpsLWT cannot replicate in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) due to induction of extensive lysosome damage and apoptosis. The mechanism of this unique infection-induced cell death remains unknown. Using a genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screening, we identified Hmg20a and Nol9 as host factors important for restricting strain Lp02rpsLWT in BMDMs. Depletion of Hmg20a protects macrophages from infection-induced lysosomal damage and apoptosis, allowing productive bacterial replication. The restriction imposed by Hmg20a was mediated by repressing the expression of several endo-lysosomal proteins, including the small GTPase Rab7. We found that SUMOylated Rab7 is recruited to the bacterial phagosome via SulF, a Dot/Icm effector that harbors a SUMO-interacting motif (SIM). Moreover, overexpression of Rab7 rescues intracellular growth of strain Lp02rpsLWT in BMDMs. Our results establish that L. pneumophila exploits the lysosomal network for the biogenesis of its phagosome in BMDMs.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Caspases; Hmg20a; Lysosomes; Rab GTPase; SUMOylation; effectors; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Legionella pneumophila exploits the endo-lysosomal network for phagosome biogenesis by co-opting SUMOylated Rab7.PLoS Pathog. 2024 May 13;20(5):e1011783. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011783. eCollection 2024 May. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38739652 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of caspase-3 by the Dot/Icm virulence system is essential for arrested biogenesis of the Legionella-containing phagosome.Cell Microbiol. 2004 Jan;6(1):33-48. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2003.00335.x. Cell Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 14678329
-
An Indispensable Role for the MavE Effector of Legionella pneumophila in Lysosomal Evasion.mBio. 2021 Feb 9;12(1):e03458-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03458-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33563829 Free PMC article.
-
[Intracellular survival and replication of legionella pneumophila within host cells].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008 Dec;128(12):1763-70. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.128.1763. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 19043295 Review. Japanese.
-
Viewing Legionella pneumophila Pathogenesis through an Immunological Lens.J Mol Biol. 2019 Oct 4;431(21):4321-4344. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.07.028. Epub 2019 Jul 25. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31351897 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
