Mentha piperita: Essential Oil and Extracts, Their Biological Activities, and Perspectives on the Development of New Medicinal and Cosmetic Products
- PMID: 37959863
- PMCID: PMC10649426
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28217444
Mentha piperita: Essential Oil and Extracts, Their Biological Activities, and Perspectives on the Development of New Medicinal and Cosmetic Products
Abstract
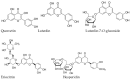
This review aims to analyze Mentha piperita L. as a potential raw material for the development of new health-promoting products (nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products). A lot of scientific publications were retrieved from the Scopus, PubMed, and Google Scholar databases which enable the study and generalization of the extraction procedures, key biologically active compounds of essential oil and extracts, biological properties, and therapeutic potential of M. piperita, along with perspectives on the development of its dosage forms, including combinations of synthetic active substances and herbal preparations of M. piperita. The results of this review indicate that M. piperita is a source rich in phytoconstituents of different chemical nature and can be regarded as a source of active substances to enhance health and to develop medicinal products for complementary therapy of various conditions, especially those related with oxidant stress, inflammation, and moderate infections. Essential oil has a broad spectrum of activities. Depending on the test and concentration, this essential oil has both anti- and prooxidant properties. Gram-positive bacteria are more sensitive to the essential oil of M. piperita than Gram-negative ones. This review also considered some facets of the standardization of essential oil and extracts of M. piperita. Among the identified phenolics of extracts were caffeic acid, rosmarinic acid, eriocitrin, luteolin derivates (luteolin-7-O-rutinoside, luteolin-7-O-glucoronide), and hesperidin. The concentration of these phenolics depends on the solvent used. This review also considered the relationships between the chemical component and biological activity. The results showed that the essential oil and extracts reduced inflammation in vitro by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), and in vivo by reducing the paw edema induced using carrageenan injection in rats. Therefore, herbal preparations of M. piperita are promising medicinal and cosmetic preparations for their usage in skincare and oral cavity care products with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing properties. This plant can also be regarded as a platform for the development of antibacterial preparations and combined anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective medicinal products (synthetic active substances plus herbal preparations). This review could be considered for the justification of the composition of some medicinal products during their pharmaceutical development for writing a registration dossier in the format of Common Technical Document.
Keywords: M. piperita; anti-inflammatory activity; antimicrobial activity; antioxidant potential; essential oil; extracts; wound-healing effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effects of Mentha piperita L. leaf essential oil against CCl4 induced hepatic oxidative damage and renal failure in rats.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jan 9;17(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0645-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29316974 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of chemical compositions and antibacterial activity of the essential oil of Mentha piperita in response to salicylic acid.Nat Prod Res. 2024 Oct;38(20):3562-3573. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2023.2256020. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Nat Prod Res. 2024. PMID: 37700677
-
Topical application of Mentha piperita essential oil accelerates wound healing in infected mice model.Inflammopharmacology. 2019 Jun;27(3):531-537. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0510-0. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Inflammopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 29980963
-
Final report on the safety assessment of Mentha Piperita (Peppermint) Oil, Mentha Piperita (Peppermint) Leaf Extract, Mentha Piperita (Peppermint) Leaf, and Mentha Piperita (Peppermint) Leaf Water.Int J Toxicol. 2001;20 Suppl 3:61-73. Int J Toxicol. 2001. PMID: 11766133 Review.
-
Mentha Pulegium: A Plant with Several Medicinal Properties.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(3):302-320. doi: 10.2174/1871530323666230914103731. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37711001 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of Botanical Extracts with Repellent and Insecticidal Activity and Their Suitability for Managing Mosquito-Borne Disease Risk in Mexico.Pathogens. 2024 Aug 29;13(9):737. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13090737. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39338928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation and olfactory loss are associated with at least 139 medical conditions.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Oct 11;17:1455418. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1455418. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39464255 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized placebo controlled trial of phytoterpenes in DMSO for the treatment of plantar fasciitis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 31;14(1):17621. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65979-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39085322 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chemical composition and toxicity of commercial Mentha spicata and Eucalyptus citriodora essential oils on Culex quinquefasciatus and non-target insects.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Mar;31(14):21610-21631. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32249-6. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38393552
-
Natural Guardians: Natural Compounds as Radioprotectors in Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 25;25(13):6937. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136937. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000045 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nilo M.C.S., Riachi L.G., Simas D.L.R., Coleho G.C., da Silva A.J.R., Costa D.C.M., Alviano D.S., Alviano C.S., De Maria C.A.B. Chemical composition and antioxidant and antifungal properties of Mentha × piperita L. (peppermint) and Mentha arvensis L. (cornmint) samples. Food Res. 2017;1:147–156. doi: 10.26656/fr.2017.5.104. - DOI
-
- Hudz N., Yezerska O., Grygorieva O., Brindza J., Felsöciová S., Kačániová M., Wieczorek P. Analytical procedure elaboration of total flavonoid content determination and antimicrobial activity of bee bread extracts. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2019;76:439–452. doi: 10.32383/appdr/103745. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wieczorek P.P., Hudz N., Yezerska O., Horčinová-Sedláčková V., Shanaida M., Korytniuk O., Jasicka-Misiak I. Chemical variability and pharmacological potential of propolis as a source for the development of new pharmaceutical products. Molecules. 2022;27:1600. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051600. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources