Modeling Liver Development and Disease in a Dish
- PMID: 37958904
- PMCID: PMC10650907
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242115921
Modeling Liver Development and Disease in a Dish
Abstract
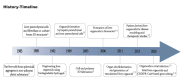
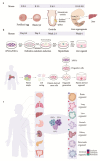
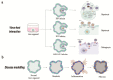
Historically, biological research has relied primarily on animal models. While this led to the understanding of numerous human biological processes, inherent species-specific differences make it difficult to answer certain liver-related developmental and disease-specific questions. The advent of 3D organoid models that are either derived from pluripotent stem cells or generated from healthy or diseased tissue-derived stem cells have made it possible to recapitulate the biological aspects of human organs. Organoid technology has been instrumental in understanding the disease mechanism and complements animal models. This review underscores the advances in organoid technology and specifically how liver organoids are used to better understand human-specific biological processes in development and disease. We also discuss advances made in the application of organoid models in drug screening and personalized medicine.
Keywords: human pluripotent stem cell; liver development; metabolic liver disease; organ-on-chip; organoids; primary liver cancer; regenerative medicine; viral infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing interest. The funding body played no role in the design, data collection, interpretation, the analysis of the study, and the writing of the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human organoids: New strategies and methods for analyzing human development and disease.Cell. 2022 Jul 21;185(15):2756-2769. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.051. Cell. 2022. PMID: 35868278 Review.
-
Disease Modeling in Stem Cell-Derived 3D Organoid Systems.Trends Mol Med. 2017 May;23(5):393-410. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Trends Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28341301 Review.
-
Disease Modeling Using 3D Organoids Derived from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 21;19(4):936. doi: 10.3390/ijms19040936. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29561796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organoid technology for brain and therapeutics research.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017 Oct;23(10):771-778. doi: 10.1111/cns.12754. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017. PMID: 28884977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling endodermal organ development and diseases using human pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids.J Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Aug 1;12(8):580-592. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjaa031. J Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32652003 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lanza R., Gearhart J., Hogan B., Melton D., Pedersen R., Thomas E.D., Thomson J., Wilmut S.I. Essentials of Stem Cell Biology. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2009.
-
- Xinaris C., Benedetti V., Rizzo P., Abbate M., Corna D., Azzollini N., Conti S., Unbekandt M., Davies J.A., Morigi M., et al. In vivo maturation of functional renal organoids formed from embryonic cell suspensions. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012;23:1857–1868. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012050505. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

