The role and mechanisms of macrophage polarization and hepatocyte pyroptosis in acute liver failure
- PMID: 37954583
- PMCID: PMC10639160
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1279264
The role and mechanisms of macrophage polarization and hepatocyte pyroptosis in acute liver failure
Abstract
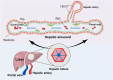
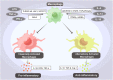
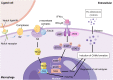
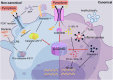
Acute liver failure (ALF) is a severe liver disease caused by disruptions in the body's immune microenvironment. In the early stages of ALF, Kupffer cells (KCs) become depleted and recruit monocytes derived from the bone marrow or abdomen to replace the depleted macrophages entering the liver. These monocytes differentiate into mature macrophages, which are activated in the immune microenvironment of the liver and polarized to perform various functions. Macrophage polarization can occur in two directions: pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages and anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. Controlling the ratio and direction of M1 and M2 in ALF can help reduce liver injury. However, the liver damage caused by pyroptosis should not be underestimated, as it is a caspase-dependent form of cell death. Inhibiting pyroptosis has been shown to effectively reduce liver damage induced by ALF. Furthermore, macrophage polarization and pyroptosis share common binding sites, signaling pathways, and outcomes. In the review, we describe the role of macrophage polarization and pyroptosis in the pathogenesis of ALF. Additionally, we preliminarily explore the relationship between macrophage polarization and pyroptosis, as well as their effects on ALF.
Keywords: acute liver failure (ALF); immune; macrophage; polarization; pyroptosis.
Copyright © 2023 Xie and Ouyang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gasdermin D-mediated hepatocyte pyroptosis expands inflammatory responses that aggravate acute liver failure by upregulating monocyte chemotactic protein 1/CC chemokine receptor-2 to recruit macrophages.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Nov 28;25(44):6527-6540. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i44.6527. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31802832 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α/HMGB1 inflammation signalling pathway regulates pyroptosis during liver failure and acute kidney injury.Cell Prolif. 2020 Jun;53(6):e12829. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12829. Epub 2020 May 17. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 32419317 Free PMC article.
-
STAT6 up-regulation amplifies M2 macrophage anti-inflammatory capacity through mesenchymal stem cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Feb;91:107266. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107266. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33321466
-
The evolving story of macrophages in acute liver failure.Immunol Lett. 2012 Sep;147(1-2):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Immunol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22820147 Review.
-
Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways.Cell Signal. 2014 Feb;26(2):192-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24219909 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage polarization: an important role in inflammatory diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 10;15:1352946. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1352946. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38660308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulatory mechanism of macrophage polarization in diabetic wound healing (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jan;31(1):2. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13367. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39422035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of ferroptosis and pyroptosis in acute liver failure.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 14;30(34):3856-3861. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3856. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39350783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin 1 in regulating the p53/glutathione peroxidase 4/gasdermin D axis in acute liver failure.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 14;30(34):3850-3855. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3850. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39350786 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of tRNA-derived small RNAs in injuries.PeerJ. 2024 Oct 24;12:e18348. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18348. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39465146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

