Macrophage polarization in osteoarthritis progression: a promising therapeutic target
- PMID: 37954210
- PMCID: PMC10639142
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1269724
Macrophage polarization in osteoarthritis progression: a promising therapeutic target
Abstract
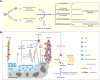
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the leading causes of pain and disability in the elderly. Synovitis, cartilage destruction and osteophyte formation histologically manifest OA. Unfortunately, there is currently no effective therapy to delay its progression and the underlying mechanisms of OA require further exploration. Macrophage is a main cellular component of joint synovium. It is highly plastic and can be stimulated to polarize to different phenotypes, namely, the pro-inflammatory phenotype (M1) and the anti-inflammatory/tissue-repairing phenotype (M2). Ample evidence has demonstrated the vital roles of macrophages in the progression of OA. Imbalanced M1/M2 ratio is significantly related to OA severity indicating macrophage polarization might be a promising therapeutic target for OA. In this review, we summarized the involvements of polarized macrophages in synovitis, cartilage degradation, osteophyte formation and OA-related chronic pain. Promising therapies targeting macrophage polarization including the intra-articular cell/derivates-based therapy and the alternative non-invasive intervention such as photobiomodulation therapy were reviewed as well.
Keywords: cell therapy; macrophage polarization; osteoarthritis; synovitis; tissue repairing.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang and Ji.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Macrophages regulate the progression of osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020 May;28(5):555-561. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2020.01.007. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020. PMID: 31982565 Review.
-
TRPV1 alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization via Ca2+/CaMKII/Nrf2 signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2021 May 18;12(6):504. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03792-8. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34006826 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage: A Potential Target on Cartilage Regeneration.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 11;11:111. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00111. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32117263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angelicin Alleviates Post-Trauma Osteoarthritis Progression by Regulating Macrophage Polarization via STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 9;12:669213. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.669213. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34177582 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of Macrophage Polarization in Osteoarthritis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies.Orthop Surg. 2024 Mar;16(3):532-550. doi: 10.1111/os.13993. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 38296798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Freeze-Thawing Treatment on Platelet-Rich Plasma Purified with Different Kits.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 16;25(18):9981. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189981. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337468 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of dental pulp stem cells by an injectable ROS-responsive hydrogel promotes temporomandibular joint cartilage repair via enhancing anti-apoptosis and regulating microenvironment.J Tissue Eng. 2024 Jun 22;15:20417314241260436. doi: 10.1177/20417314241260436. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2024. PMID: 38911101 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning analysis of serum cholesterol's impact on knee osteoarthritis progression.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 14;14(1):18852. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69906-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39143135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alves A. C., Vieira R., Leal-Junior E., dos Santos S., Ligeiro A. P., Albertini R., et al. (2013). Effect of low-level laser therapy on the expression of inflammatory mediators and on neutrophils and macrophages in acute joint inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 15, R116. 10.1186/ar4296 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amaroli A., Ravera S., Baldini F., Benedicenti S., Panfoli I., Vergani L. (2019). Photobiomodulation with 808-nm diode laser light promotes wound healing of human endothelial cells through increased reactive oxygen species production stimulating mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Lasers Med. Sci. 34, 495–504. 10.1007/s10103-018-2623-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ayral X., Pickering E., Woodworth T., Mackillop N., Dougados M. (2005). Synovitis: a potential predictive factor of structural progression of medial tibiofemoral knee osteoarthritis -- results of a 1 year longitudinal arthroscopic study in 422 patients. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 13, 361–367. 10.1016/j.joca.2005.01.005 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

