AGC kinase inhibitors regulate STING signaling through SGK-dependent and SGK-independent mechanisms
- PMID: 37939709
- PMCID: PMC10842197
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.10.008
AGC kinase inhibitors regulate STING signaling through SGK-dependent and SGK-independent mechanisms
Abstract
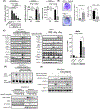
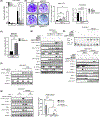
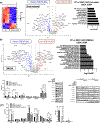
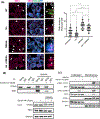
Type 1 IFN expression is critical in the innate immune response, but aberrant expression is associated with autoimmunity and cancer. Here, we identify N-[4-(1H46 pyrazolo[3,4-b] pyrazin-6-yl)-phenyl]-sulfonamide (Sanofi-14h), a compound with preference for inhibition of the AGC family kinase SGK3, as an inhibitor of Ifnb1 gene expression in response to STING stimulation of macrophages. Sanofi-14h abrogated SGK activity and also impaired activation of the critical TBK1/IRF3 pathway downstream of STING activation, blocking interaction of STING with TBK1. Deletion of SGK1/3 in a macrophage cell line did not block TBK1/IRF3 activation but decreased expression of transcription factors, such as IRF7 and STAT1, required for the innate immune response. Other AGC kinase inhibitors blocked TBK1 and IRF3 activation suggesting common action on a critical regulatory node in the STING pathway. These studies reveal both SGK-dependent and SGK-independent mechanisms in the innate immune response and indicate an approach to block aberrant Ifnb1 expression.
Keywords: AGC kinases; IRF; SGK; STING; Sanofi-14h; TBK1; double strand DNA viral response; innate immunity; interferon; interferon regulatory factor; macrophages; serum and glucocorticoid kinase; stimulator of interferon genes; tank binding kinase.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
STING specifies IRF3 phosphorylation by TBK1 in the cytosolic DNA signaling pathway.Sci Signal. 2012 Mar 6;5(214):ra20. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002521. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22394562 Free PMC article.
-
The cGas-Sting Signaling Pathway Is Required for the Innate Immune Response Against Ectromelia Virus.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 14;9:1297. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01297. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29963044 Free PMC article.
-
TBK1 and IKKε Act Redundantly to Mediate STING-Induced NF-κB Responses in Myeloid Cells.Cell Rep. 2020 Apr 7;31(1):107492. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.03.056. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32268090
-
Potential Therapeutic Value of the STING Inhibitors.Molecules. 2023 Mar 31;28(7):3127. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073127. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TBK1 is paradoxical in tumor development: a focus on the pathway mediating IFN-I expression.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 5;15:1433321. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1433321. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39161768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

