Study of fingolimod, nitric oxide inhibitor, and P-glycoprotein inhibitor in modulating the P-glycoprotein expression via an endothelin-sphingolipid pathway in an animal model of pharmacoresistant epilepsy
- PMID: 37929409
- PMCID: PMC10751529
- DOI: 10.4103/ijp.ijp_100_23
Study of fingolimod, nitric oxide inhibitor, and P-glycoprotein inhibitor in modulating the P-glycoprotein expression via an endothelin-sphingolipid pathway in an animal model of pharmacoresistant epilepsy
Abstract
Background: The overexpression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) contributes to drug resistance in patients with epilepsy, and the change of P-gp expression located at the blood-brain barrier alienates the anti-seizure effects of P-gp substrates. Thus, the present study explored the effect of fingolimod (FTY720) acting through an endothelin-sphingolipid pathway on P-gp-induced pentylenetetrazol (PTZ)-kindled phenobarbital (PB)-resistant rats.
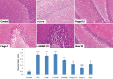
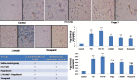
Materials and methods: PTZ kindling (30 mg/kg; i.p.) and PB (40 mg/kg; orally) were used to develop an animal model of refractory epilepsy. The effect of Fingolimod on seizure score (Racine scale), plasma and brain levels of PB (high-performance liquid chromatography), and blood-brain barrier permeability (Evans blue dye) was determined. Further, Fingolimod's neuroprotective effect was determined by measuring the levels of various inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress parameters, and neurotrophic factors in rat brain homogenate. The Fingolimod's effect on P-gp expression was estimated by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry in rat brain. The H and E staining was done to determine the neuronal injury.
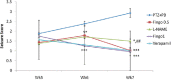
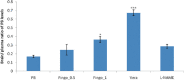
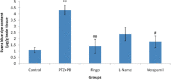
Results: Fingolimod significantly (P < 0.001) reduced the seizure score in a dose-dependent manner and alleviated the blood-brain barrier permeability. It decreased the P-gp expression, which further increased the brain PB concentration. Fingolimod significantly (P < 0.01) reduced oxidative stress as well as inflammation. Moreover, it attenuated the raised neuronal injury score in a resistant model of epilepsy.
Conclusion: The modulation of the P-gp expression by Fingolimod improved drug delivery to the brain in an animal model of refractory epilepsy. Therefore, S1P signaling could serve as an additional therapeutic target to overcome refractoriness.
Keywords: Fingolimod; P-glycoprotein; neuroprotection; phenobarbital resistance; refractory epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Analogue FTY720 Alleviates Seizure-induced Overexpression of P-Glycoprotein in Rat Hippocampus.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Jul;123(1):14-20. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12973. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29380527
-
Targeting blood-brain barrier sphingolipid signaling reduces basal P-glycoprotein activity and improves drug delivery to the brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 25;109(39):15930-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203534109. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22949658 Free PMC article.
-
Fingolimod enhances myelin repair of hippocampus in pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling model.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017 Jan 1;96:72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2016.09.016. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 27634580
-
ABC transporters during epilepsy and mechanisms underlying multidrug resistance in refractory epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2007;48 Suppl 5:140-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01302.x. Epilepsia. 2007. PMID: 17910594 Review.
-
A Novel Approach to Refractory Epilepsy by Targeting Pgp Peripherally and Centrally: Therapeutic Targets and Future Perspectives.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2020;19(10):741-749. doi: 10.2174/1871527319999200819093109. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32814543 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Fingolimod on Psychological Symptoms and Cognitive Function in Neuropsychiatric and Neurological Disorders.Neurochem Res. 2024 Oct;49(10):2668-2681. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04199-5. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38918332 Review.
References
-
- Sisodiya SM, Martinian L, Scheffer GL, van der Valk P, Scheper RJ, Harding BN, et al. Vascular colocalization of P-glycoprotein, multidrug-resistance associated protein 1, breast cancer resistance protein and major vault protein in human epileptogenic pathologies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2006;32:51–63. - PubMed
-
- Krishna R, St-Louis M, Mayer LD. Increased intracellular drug accumulation and complete chemosensitization achieved in multidrug-resistant solid tumors by co-administering valspodar (PSC 833) with sterically stabilized liposomal doxorubicin. Int J Cancer. 2000;85:131–41. - PubMed
-
- Liang XJ, Aszalos A. Multidrug transporters as drug targets. Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7:911–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

