Sigma-1 Receptor Inhibition Reduces Mechanical Allodynia and Modulate Neuroinflammation in Chronic Neuropathic Pain
- PMID: 37922065
- PMCID: PMC11043107
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-023-03717-w
Sigma-1 Receptor Inhibition Reduces Mechanical Allodynia and Modulate Neuroinflammation in Chronic Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
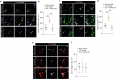
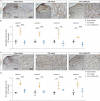
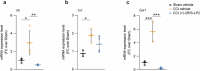
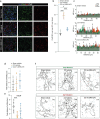
Neuropathic pain is one of the most debilitating forms of chronic pain, resulting from an injury or disease of the somatosensory nervous system, which induces abnormal painful sensations including allodynia and hyperalgesia. Available treatments are limited by severe side-effects and reduced efficacy in the chronic phase of the disease. Sigma-1 receptor (σ1R) has been identified as a chaperone protein, which modulate opioid receptors activities and the functioning of several ion channels, exerting a role in pain transmission. As such, it represents a druggable target to treat neuropathic pain. This study aims at investigating the therapeutic potential of the novel compound (+)-2R/S-LP2, a σ1R antagonist, in reducing painful behaviour and modulating the neuroinflammatory environment. We showed that repeated administration of the compound significantly inhibited mechanical allodynia in neuropathic rats, increasing the withdrawal threshold as compared to CCI-vehicle rats. Moreover, we found that (+)-2R/S-LP2-mediated effects resolve the neuroinflammatory microenvironment by reducing central gliosis and pro-inflammatory cytokines expression levels. This effect was coupled with a significant reduction of connexin 43 (Cx43) expression levels and gap junctions/hemichannels mediated microglia-to-astrocyte communication. These results suggest that inhibition of σ1R significantly attenuates neuropathic pain chronicization, thus representing a viable effective strategy.
Keywords: Astrocyte; Connexin 43; Gap junction; Microglia; Neuropathic pain; Sigma-1.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sigma-1 receptor targeting inhibits connexin 43 based intercellular communication in chronic neuropathic pain.Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct;73(10):1711-1726. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01926-0. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39095656 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte sigma-1 receptors modulate connexin 43 expression leading to the induction of below-level mechanical allodynia in spinal cord injured mice.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Dec;111:34-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.08.027. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27567941
-
Simultaneous Activation of Mu and Delta Opioid Receptors Reduces Allodynia and Astrocytic Connexin 43 in an Animal Model of Neuropathic Pain.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Nov;56(11):7338-7354. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-1607-1. Epub 2019 Apr 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31030416
-
Sigma-1 receptor: A drug target for the modulation of neuroimmune and neuroglial interactions during chronic pain.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jan;163:105339. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105339. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33276102 Review.
-
Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonists: A New Class of Neuromodulatory Analgesics.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;964:109-132. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50174-1_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28315268 Review.
Cited by
-
Intravesical Botulinum Toxin Injection Plus Hydrodistention Is More Effective in Patients with Bladder Pain-Predominant Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Feb 1;16(2):74. doi: 10.3390/toxins16020074. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38393152 Free PMC article.
-
Novel drug treatments for pain in advanced cancer and serious illness: a focus on neuropathic pain and chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.Palliat Care Soc Pract. 2024 Jul 31;18:26323524241266603. doi: 10.1177/26323524241266603. eCollection 2024. Palliat Care Soc Pract. 2024. PMID: 39086469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions and Trends of Interleukins, PAI-1, CRP, and TNF-α in Inflammatory Responses during the Perioperative Period of Joint Arthroplasty: Implications for Pain Management-A Narrative Review.J Pers Med. 2024 May 17;14(5):537. doi: 10.3390/jpm14050537. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38793119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sigma-1 receptor targeting inhibits connexin 43 based intercellular communication in chronic neuropathic pain.Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct;73(10):1711-1726. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01926-0. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39095656 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

