The Importance of Basal Cell Carcinoma Risk Stratification and Potential Future Pathways
- PMID: 37902813
- PMCID: PMC10644189
- DOI: 10.2196/50309
The Importance of Basal Cell Carcinoma Risk Stratification and Potential Future Pathways
Abstract
Background: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common human cancer. Although there are surgical and topical treatments available, surgery remains the mainstay of treatment, leading to higher costs. What is needed is an accurate risk assessment of BCC so that treatments can be planned in a patient-centered manner.
Objective: In this study, we will review the literature about guidelines for the management of BCC and analyze the potential indicators of high-risk BCC. Using this risk assessment approach, we will propose pathways that will be able to optimize treatments more efficiently.
Methods: This paper presents a perspective from a skin cancer expert and clinic involved in the treatment of both simple and complex cases of BCC. It addresses the key challenges associated with accurate risk stratification prior to any treatment or procedure. Different immunohistochemical and angiogenic markers for high-risk BCC were reviewed in this study.
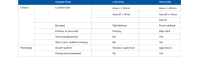
Results: The expression of interleukin-6, vascular endothelial growth factor, and mast cells within BCC correlates with its aggressiveness. Other immunohistochemical markers, such as Cyclin D1 and Bcl-2, also play a significant role-Cyclin D1 is higher in the aggressive BCC, while Bcl-2 is lower in the aggressive BCC, compared to the nonaggressive variants.
Conclusions: Based on our research, we will conclude that using immunohistochemical and angiogenic markers for risk assessment and stratification of BCC can help optimize treatment, ensuring that surgical procedures are used only when necessary.
Keywords: BCC; angiogenic; angiogenic agents; angiogenic marker; basal cell carcinoma; cancer; carcinoma; dermatology; histology; immunohistochemistry; management; markers; risk assessment; skin; skin cancer; surgery; tumour markers.
©Sharad Paul, Allanah Knight. Originally published in JMIR Dermatology (http://derma.jmir.org), 30.10.2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exfoliative cytology for diagnosing basal cell carcinoma and other skin cancers in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 4;12(12):CD013187. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013187. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30521689 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of p16 Protein in Cutaneous Basal Cell Carcinoma: Still far from Being Clearly Understood.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2020 Jul;28(1):43-44. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2020. PMID: 32650852
-
The Effects of Cyclin D1 and Bcl-2 Expressıon on Aggressive Behavior in Basal Cell and Basosquamous Carcinoma.Iran J Pathol. 2015 Summer;10(3):185-91. Iran J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26351483 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma: European consensus-based interdisciplinary guidelines.Eur J Cancer. 2019 Sep;118:10-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Eur J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31288208 Review.
-
Basal cell carcinoma: an evidence-based treatment update.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014 Jul;15(3):197-216. doi: 10.1007/s40257-014-0070-z. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24733429 Review.
References
-
- McDaniel B, Badri T, Steele RB. Basal Cell Carcinoma. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Sep 19, pp. 1–21. - PubMed
-
- Trakatelli Myrto, Morton C, Nagore E, Ulrich C, Del Marmol Veronique, Peris Ketty, Basset-Seguin Nicole, BCC subcommittee of the Guidelines Committee of the European Dermatology Forum Update of the European guidelines for basal cell carcinoma management. Eur J Dermatol. 2014;24(3):312–29. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2014.2271.ejd.2014.2271 - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Loo E, Mosterd K, Krekels GA, Roozeboom MH, Ostertag JU, Dirksen CD, Steijlen PM, Neumann HM, Nelemans PJ, Kelleners-Smeets NW. Surgical excision versus Mohs' micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face: a randomised clinical trial with 10 year follow-up. Eur J Cancer. 2014 Nov;50(17):3011–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.08.018.S0959-8049(14)00913-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Crowson AN. Basal cell carcinoma: biology, morphology and clinical implications. Mod Pathol. 2006 Mar;19 Suppl 2:S127–47. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800512. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0893-3952(22)03428-7 S0893-3952(22)03428-7 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

