Polysaccharide-Based Nanogels to Overcome Mucus, Skin, Cornea, and Blood-Brain Barriers: A Review
- PMID: 37896268
- PMCID: PMC10610445
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102508
Polysaccharide-Based Nanogels to Overcome Mucus, Skin, Cornea, and Blood-Brain Barriers: A Review
Abstract
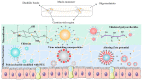
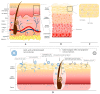
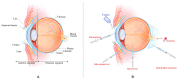
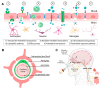
Nanocarriers have been extensively developed in the biomedical field to enhance the treatment of various diseases. However, to effectively deliver therapeutic agents to desired target tissues and enhance their pharmacological activity, these nanocarriers must overcome biological barriers, such as mucus gel, skin, cornea, and blood-brain barriers. Polysaccharides possess qualities such as excellent biocompatibility, biodegradability, unique biological properties, and good accessibility, making them ideal materials for constructing drug delivery carriers. Nanogels, as a novel drug delivery platform, consist of three-dimensional polymer networks at the nanoscale, offering a promising strategy for encapsulating different pharmaceutical agents, prolonging retention time, and enhancing penetration. These attractive properties offer great potential for the utilization of polysaccharide-based nanogels as drug delivery systems to overcome biological barriers. Hence, this review discusses the properties of various barriers and the associated constraints, followed by summarizing the most recent development of polysaccharide-based nanogels in drug delivery to overcome biological barriers. It is expected to provide inspiration and motivation for better design and development of polysaccharide-based drug delivery systems to enhance bioavailability and efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Keywords: biological barriers; drug delivery; nanocarriers; nanogel; polysaccharides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crossing biological barriers with nanogels to improve drug delivery performance.J Control Release. 2019 Aug 10;307:221-246. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.06.005. Epub 2019 Jun 5. J Control Release. 2019. PMID: 31175895 Review.
-
Polysaccharide based nanogels in the drug delivery system: Application as the carrier of pharmaceutical agents.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016 Nov 1;68:964-981. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.05.121. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016. PMID: 27524098 Review.
-
Nanogels as novel drug nanocarriers for CNS drug delivery.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Aug 8;10:1232109. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1232109. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37621994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart stimuli-responsive polysaccharide nanohydrogels for drug delivery: a review.J Mater Chem B. 2023 Nov 15;11(44):10538-10565. doi: 10.1039/d3tb01712e. J Mater Chem B. 2023. PMID: 37909361 Review.
-
The Application of Nanogels as Efficient Drug Delivery Platforms for Dermal/Transdermal Delivery.Gels. 2023 Sep 15;9(9):753. doi: 10.3390/gels9090753. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37754434 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in nanogels for drug delivery and biomedical applications.Biomater Sci. 2024 Nov 19;12(23):6006-6018. doi: 10.1039/d4bm00224e. Biomater Sci. 2024. PMID: 39484856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanostructure-Mediated Transport of Therapeutics through Epithelial Barriers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 28;25(13):7098. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137098. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000205 Free PMC article. Review.

