Combination of Phenethyl Isothiocyanate and Dasatinib Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastatic Potential through FAK/STAT3/Cadherin Signalling and Reduction of VEGF Secretion
- PMID: 37896150
- PMCID: PMC10610226
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102390
Combination of Phenethyl Isothiocyanate and Dasatinib Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastatic Potential through FAK/STAT3/Cadherin Signalling and Reduction of VEGF Secretion
Abstract
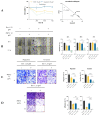
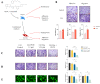
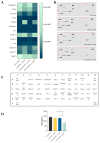
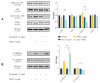
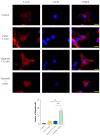
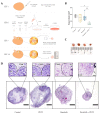
Cancerous cells are characterised by their ability to invade, metastasise, and induce angiogenesis. Tumour cells use various molecules that can be targeted to reverse these processes. Dasatinib, a potent Src inhibitor, has shown promising results in treating hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in vitro and in vivo. However, its effectiveness is limited by focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation. Isothiocyanates, on the other hand, are phytochemicals with broad anticancer activity and FAK inhibition capabilities. This study evaluated the synergistic effect of dasatinib and phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) on HCC. The combination was tested using various assays, including MTT, adhesion, scratch, Boyden chamber, chorioallantoic membrane (CAM), and yolk sac membrane (YSM) assays to evaluate the effect of the drug combination on HCC metastatic potential and angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. The results showed that the combination inhibited the adhesion, migration, and invasion of HepG2 cells and reduced xenograft volume in the CAM assay. Additionally, the combination reduced angiogenesis in vitro, diminishing the growth of vessels in the tube formation assay. The inhibition of FAK/STAT3 signalling led to increased E-cadherin expression and reduced VEGF secretion, reducing HCC metastatic potential. Therefore, a combination of PEITC and dasatinib could be a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of HCC.
Keywords: CAM assay; FAK; HCC; PEITC; VEGF; cancer therapeutics; combination therapy; dasatinib; drug development; oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of SRC/FAK cue: A novel pathway for the synergistic effect of rosuvastatin on the anti-cancer effect of dasatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma.Life Sci. 2018 Nov 15;213:248-257. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30292831
-
Phenethyl isothiocyanate and dasatinib combination synergistically reduces hepatocellular carcinoma growth via cell cycle arrest and oxeiptosis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 4;14:1264032. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1264032. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37860118 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of action and potential biomarkers of growth inhibition of dasatinib (BMS-354825) on hepatocellular carcinoma cells.BMC Cancer. 2013 May 30;13:267. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-267. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23721490 Free PMC article.
-
Phenethyl isothiocyanate inhibits migration and invasion of human gastric cancer AGS cells through suppressing MAPK and NF-kappaB signal pathways.Anticancer Res. 2010 Jun;30(6):2135-43. Anticancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20651362
-
Phenethyl isothiocyanate inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and ex vivo.Cancer Res. 2007 Mar 1;67(5):2239-46. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3645. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17332354
Cited by
-
Dietary isothiocyanates and anticancer agents: exploring synergism for improved cancer management.Front Nutr. 2024 Jun 11;11:1386083. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1386083. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38919393 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Calderon-Martinez E., Landazuri-Navas S., Vilchez E., Cantu-Hernandez R., Mosquera-Moscoso J., Encalada S., Al Lami Z., Zevallos-Delgado C., Cinicola J. Prognostic Scores and Survival Rates by Etiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2023;15:200–207. doi: 10.14740/jocmr4902. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

