Activation of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex Contributes to Neuropathic Pain
- PMID: 37895135
- PMCID: PMC10607712
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242015454
Activation of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex Contributes to Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
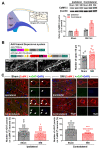
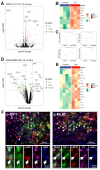
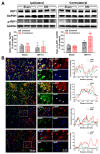
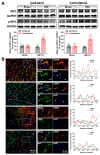
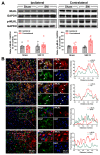
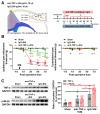
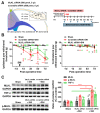
The hyperexcitability of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) has been implicated in the development of chronic pain. As one of the key causes of ACC hyperexcitation, disinhibition of the ACC may be closely related to the dysfunction of inhibitory parvalbumin (PV)-expressing interneurons (PV-INs). However, the molecular mechanism underlying the ACC PV-INs injury remains unclear. The present study demonstrates that spared sciatic nerve injury (SNI) induces an imbalance in the excitation and inhibition (E/I) of the ACC. To test whether tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) upregulation in the ACC after SNI activates necroptosis and participates in PV-INs damage, we performed a differential analysis of transcriptome sequencing using data from neuropathic pain models and found that the expression of genes key to the TNF-α-necroptosis pathway were upregulated. TNF-α immunoreactivity (IR) signals in the ACCs of SNI rats were co-located with p-RIP3- and PV-IR, or p-MLKL- and PV-IR signals. We then systematically detected the expression and cell localization of necroptosis-related proteins, including kinase RIP1, RIP3, MLKL, and their phosphorylated states, in the ACC of SNI rats. Except for RIP1 and MLKL, the levels of these proteins were significantly elevated in the contralateral ACC and mainly expressed in PV-INs. Blocking the ACC TNF-α-necroptosis pathway by microinjecting TNF-α neutralizing antibody or using an siRNA knockdown to block expression of MLKL in the ACC alleviated SNI-induced pain hypersensitivity and inhibited the upregulation of TNF-α and p-MLKL. Targeting TNF-α-triggered necroptosis within ACC PV-INs may help to correct PV-INs injury and E/I imbalance in the ACC in neuropathic pain.
Keywords: anterior cingulate cortex; necroptosis; neuropathic pain; parvalbumin interneuron; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NLRP3-Mediated Piezo1 Upregulation in ACC Inhibitory Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons Is Involved in Pain Processing after Peripheral Nerve Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13035. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113035. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361825 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the anterior cingulate cortex contributes to neuropathic pain and pain-associated aversion.Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Oct;130:104456. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 31028871
-
Resveratrol inhibits necroptosis by mediating the TNF-α/RIP1/RIP3/MLKL pathway in myocardial hypoxia/reoxygenation injury.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Mar 26;53(4):430-437. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmab012. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 33686403
-
Neuroimmune Mechanisms Underlying Neuropathic Pain: The Potential Role of TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 28;23(13):7191. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137191. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Necroptosis in health and diseases.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Nov;35:14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.07.013. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25087983 Review.
Cited by
-
Interactions and Trends of Interleukins, PAI-1, CRP, and TNF-α in Inflammatory Responses during the Perioperative Period of Joint Arthroplasty: Implications for Pain Management-A Narrative Review.J Pers Med. 2024 May 17;14(5):537. doi: 10.3390/jpm14050537. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38793119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Cisplatin promotes TNF-α autocrine to trigger RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-dependent necroptosis of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Oct 20;44(10):1947-1954. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.13. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39523095 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Chen T., Taniguchi W., Chen Q.Y., Tozaki-Saitoh H., Song Q., Liu R.H., Koga K., Matsuda T., Kaito-Sugimura Y., Wang J., et al. Top-down descending facilitation of spinal sensory excitatory transmission from the anterior cingulate cortex. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:1886. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04309-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Q.Y., Chen S.X., Liu J.Y., Yao P.W., Duan Y.W., Li Y.Y., Zang Y. Neuroinflammation in the anterior cingulate cortex: The potential supraspinal mechanism underlying the mirror-image pain following motor fiber injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022;19:162. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02525-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

