Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: From Uncovered Resistance Mechanisms to Current Treatments
- PMID: 37894414
- PMCID: PMC10605314
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15205047
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: From Uncovered Resistance Mechanisms to Current Treatments
Abstract
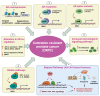
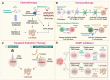
Prostate cancer (PC) is the second most common cancer in men worldwide. Despite recent advances in diagnosis and treatment, castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) remains a significant medical challenge. Prostate cancer cells can develop mechanisms to resist androgen deprivation therapy, such as AR overexpression, AR mutations, alterations in AR coregulators, increased steroidogenic signaling pathways, outlaw pathways, and bypass pathways. Various treatment options for CRPC exist, including androgen deprivation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, localized or systemic therapeutic radiation, and PARP inhibitors. However, more research is needed to combat CRPC effectively. Further investigation into the underlying mechanisms of the disease and the development of new therapeutic strategies will be crucial in improving patient outcomes. The present work summarizes the current knowledge regarding the underlying mechanisms that promote CRPC, including both AR-dependent and independent pathways. Additionally, we provide an overview of the currently approved therapeutic options for CRPC, with special emphasis on chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, PARP inhibitors, and potential combination strategies.
Keywords: PARP inhibitors; androgen deprivation therapy (ADT); androgen signaling; castration-resistant prostate cancer; chemotherapy; immunotherapy; radionuclide therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Androgen receptor-dependent and -independent mechanisms driving prostate cancer progression: Opportunities for therapeutic targeting from multiple angles.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3724-3745. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12554. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27741508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).Transl Androl Urol. 2015 Jun;4(3):365-80. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.05.02. Transl Androl Urol. 2015. PMID: 26814148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Regulation of Androgen Receptor in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Premises, Promises, and Potentials.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 25;14(4):559-569. doi: 10.2174/1874467213666201223121850. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33357209 Review.
-
Understanding Mechanisms of Resistance in Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer: The Role of the Androgen Receptor.Eur Urol Focus. 2016 Dec;2(5):499-505. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2016.11.013. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Eur Urol Focus. 2016. PMID: 28723515 Review.
-
Targeting the androgen receptor signaling pathway in advanced prostate cancer.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2022 Jul 22;79(15):1224-1235. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/zxac105. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35390118 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling molecular characteristics and tumor microenvironment dynamics of neuroendocrine prostate cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Oct 16;150(10):462. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05983-0. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39412660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The changing face of castrate resistant prostate cancer.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2024 Sep 19. doi: 10.1038/s41391-024-00895-z. Online ahead of print. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2024. PMID: 39300288 No abstract available.
-
Sialylation Inhibition Can Partially Revert Acquired Resistance to Enzalutamide in Prostate Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 24;16(17):2953. doi: 10.3390/cancers16172953. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272811 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a small-molecule NDR1 agonist for prostate cancer therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 12;15:1367358. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1367358. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38410130 Free PMC article.
-
Gender-affirming hormone therapy in transgender women and risk of prostate cancer: pathophysiological mechanisms and clinical implications.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2024 Jan 31. doi: 10.1038/s41391-024-00796-1. Online ahead of print. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2024. PMID: 38297151 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Scher H.I., Morris M.J., Stadler W.M., Higano C.S., Halabi S., Smith M.R., Basch E.M., Fizazi K., Ryan C.J., Antonarakis E.S., et al. The Prostate Cancer Working Group 3 (PCWG3) Consensus for Trials in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC) J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;33:5000. doi: 10.1200/jco.2015.33.15_suppl.5000. - DOI
-
- Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Mechanisms, Targets and Treatment. SpringerLink. [(accessed on 24 May 2023)]. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-99286-0_7. - DOI
-
- Eisenhauer E.A., Therasse P., Bogaerts J., Schwartz L.H., Sargent D., Ford R., Dancey J., Arbuck S., Gwyther S., Mooney M., et al. New Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours: Revised RECIST Guideline (Version 1.1) Eur. J. Cancer. 2009;45:228–247. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

