Astaxanthin: Past, Present, and Future
- PMID: 37888449
- PMCID: PMC10608541
- DOI: 10.3390/md21100514
Astaxanthin: Past, Present, and Future
Abstract
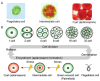
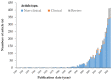
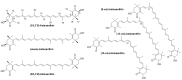
Astaxanthin (AX), a lipid-soluble pigment belonging to the xanthophyll carotenoids family, has recently garnered significant attention due to its unique physical properties, biochemical attributes, and physiological effects. Originally recognized primarily for its role in imparting the characteristic red-pink color to various organisms, AX is currently experiencing a surge in interest and research. The growing body of literature in this field predominantly focuses on AXs distinctive bioactivities and properties. However, the potential of algae-derived AX as a solution to various global environmental and societal challenges that threaten life on our planet has not received extensive attention. Furthermore, the historical context and the role of AX in nature, as well as its significance in diverse cultures and traditional health practices, have not been comprehensively explored in previous works. This review article embarks on a comprehensive journey through the history leading up to the present, offering insights into the discovery of AX, its chemical and physical attributes, distribution in organisms, and biosynthesis. Additionally, it delves into the intricate realm of health benefits, biofunctional characteristics, and the current market status of AX. By encompassing these multifaceted aspects, this review aims to provide readers with a more profound understanding and a robust foundation for future scientific endeavors directed at addressing societal needs for sustainable nutritional and medicinal solutions. An updated summary of AXs health benefits, its present market status, and potential future applications are also included for a well-rounded perspective.
Keywords: SDGs; anti-aging; astaxanthin; commercial production; microalgae; mitochondria; slow-aging.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.N. is employed by Fuji Chemical Industries, Co., Ltd. P.B. and B.S. are employed by AstaReal AB. K.H. is employed by AstaReal, Inc. All other authors declare that there is no duality of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures

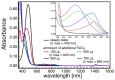
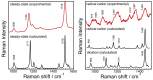
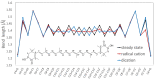
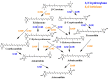

Similar articles
-
Astaxanthin: a review of its chemistry and applications.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2006;46(2):185-96. doi: 10.1080/10408690590957188. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16431409 Review.
-
Dietary astaxanthin: an excellent carotenoid with multiple health benefits.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(18):3019-3045. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1983766. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 34581210 Review.
-
Microbial astaxanthin: from bioprocessing to the market recognition.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jul;107(13):4199-4215. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12586-1. Epub 2023 May 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37233757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioaccessibility of Marine Carotenoids.Mar Drugs. 2018 Oct 22;16(10):397. doi: 10.3390/md16100397. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30360450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ketocarotenoids adonirubin and adonixanthin: Properties, health benefits, current technologies, and emerging challenges.Food Chem. 2024 Jun 15;443:138610. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138610. Epub 2024 Jan 28. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38301562 Review.
Cited by
-
Astaxanthin, Compared to Other Carotenoids, Increases the Efficacy of Methotrexate in Rat Adjuvant Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 9;25(16):8710. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168710. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201397 Free PMC article.
-
Can Nutraceuticals Support the Treatment of MASLD/MASH, and thus Affect the Process of Liver Fibrosis?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 11;25(10):5238. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105238. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Lysophosphatidylcholine Improves the Uptake of Astaxanthin and Modulates Cholesterol Transport in Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 23;13(5):505. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050505. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790610 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction and Synthesis of Typical Carotenoids: Lycopene, β-Carotene, and Astaxanthin.Molecules. 2024 Sep 25;29(19):4549. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194549. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Study on the Effect of Various Media and the Supplementation of Organic Compounds on the Enhanced Production of Astaxanthin from Haematococcus lacustris (Girod-Chantrans) Rostafinski (Chlorophyta).Microorganisms. 2024 May 21;12(6):1040. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061040. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grand View Research Inc Astaxanthin Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Product (Oil, Softgel, Liquid), By Source (Natural, Synthetic), By Application (Aquaculture & Animal Feed, Nutraceuticals), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2021. 2021. [(accessed on 1 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/global-astaxanthin-m....
-
- MarketsandMarkets Research Pvt., L. Astaxanthin Market Global Forecast To. [(accessed on 1 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/astaxanthin-market-1621....
-
- Research E.M. Global Astaxanthin Market: By Product: Dried Algae Meal or Biomass, Oil, Softgel, Liquid, Others; By Source: Natural, Synthetic; By Application: Aquaculture and Animal Feed, Nutraceuticals, Others; Regional Analysis; Historical Market and Forecast (2018–2028); Market Dynamics; Competitive Landscape; Industry Events and Developments. [(accessed on 1 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/astaxanthin-market.
-
- Britton G., Liaaen-Jensen S., Pfander H. Carotenoids. Handbook. Springer; New York City, NY, USA: 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

