Recognition and coacervation of G-quadruplexes by a multifunctional disordered region in RECQ4 helicase
- PMID: 37875529
- PMCID: PMC10598209
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42503-z
Recognition and coacervation of G-quadruplexes by a multifunctional disordered region in RECQ4 helicase
Abstract
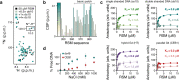
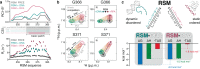
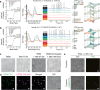
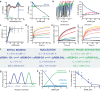
Biomolecular polyelectrolyte complexes can be formed between oppositely charged intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) of proteins or between IDRs and nucleic acids. Highly charged IDRs are abundant in the nucleus, yet few have been functionally characterized. Here, we show that a positively charged IDR within the human ATP-dependent DNA helicase Q4 (RECQ4) forms coacervates with G-quadruplexes (G4s). We describe a three-step model of charge-driven coacervation by integrating equilibrium and kinetic binding data in a global numerical model. The oppositely charged IDR and G4 molecules form a complex in the solution that follows a rapid nucleation-growth mechanism leading to a dynamic equilibrium between dilute and condensed phases. We also discover a physical interaction with Replication Protein A (RPA) and demonstrate that the IDR can switch between the two extremes of the structural continuum of complexes. The structural, kinetic, and thermodynamic profile of its interactions revealed a dynamic disordered complex with nucleic acids and a static ordered complex with RPA protein. The two mutually exclusive binding modes suggest a regulatory role for the IDR in RECQ4 function by enabling molecular handoffs. Our study extends the functional repertoire of IDRs and demonstrates a role of polyelectrolyte complexes involved in G4 binding.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


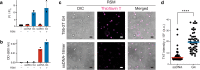
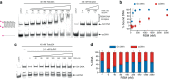
Similar articles
-
Binding without folding - the biomolecular function of disordered polyelectrolyte complexes.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2020 Feb;60:66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2019.12.006. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 31874413 Review.
-
Self-Assembling Polypeptides in Complex Coacervation.Acc Chem Res. 2024 Feb 6;57(3):386-398. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00689. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38252962
-
Computational insights into intrinsically disordered regions in protein-nucleic acid complexes.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Oct;277(Pt 1):134021. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134021. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39032884
-
Features of molecular recognition of intrinsically disordered proteins via coupled folding and binding.Protein Sci. 2019 Nov;28(11):1952-1965. doi: 10.1002/pro.3718. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Protein Sci. 2019. PMID: 31441158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A guanine-flipping and sequestration mechanism for G-quadruplex unwinding by RecQ helicases.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 10;9(1):4201. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06751-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30305632 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predicting nuclear G-quadruplex RNA-binding proteins with roles in transcription and phase separation.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 22;15(1):2585. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46731-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38519458 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

