Characterization of SNCA Multiplication in Parkinson's Disease: 2 New Cases and Evaluation of the Literature
- PMID: 37868923
- PMCID: PMC10585967
- DOI: 10.1002/mdc3.13852
Characterization of SNCA Multiplication in Parkinson's Disease: 2 New Cases and Evaluation of the Literature
Abstract
Background: Alpha-synuclein (SNCA) copy number variations (CNV) have been certified as a causative mutation in patients with familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease (PD).
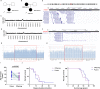
Case: We report three SNCA duplication cases diagnosed as PD. Through whole-exome sequencing, we identified a de novo 4.56 Mb repeated region in one patient and a 2.50 Mb repeated region in familial PD with two patients.
Literature review: In review of previous cases, we suggest that aggressive behavior is more remarkable in CNV4 patients. Meanwhile, frequency of cognition decline and dementia were slightly increased in CNV4 patients. We also illustrate a younger onset age in offspring than parent in familial SNCA multiplication PD cases. No difference was observed in disease duration between parent and offspring generation.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrated the clinical and genetic characteristics in PD with SNCA multiplication and provided strong evidence for genetic anticipation. These results may be instructive for future disease diagnosis and genetic counseling.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; SNCA; copy number variation; genotype–phenotype.
© 2023 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Meta-Analysis of α-Synuclein Multiplication in Familial Parkinsonism.Front Neurol. 2018 Dec 11;9:1021. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.01021. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30619023 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Analysis and Literature Review of SNCA Variants in Parkinson's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Aug 12;13:648151. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.648151. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34456707 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel SNCA A30G Mutation Causes Familial Parkinson's Disease.Mov Disord. 2021 Jul;36(7):1624-1633. doi: 10.1002/mds.28534. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Mov Disord. 2021. PMID: 33617693
-
[Relationship between alpha-synuclein and Parkinson's disease].Brain Nerve. 2007 Aug;59(8):825-30. Brain Nerve. 2007. PMID: 17713118 Review. Japanese.
-
Autosomal dominant Parkinson's disease caused by SNCA duplications.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016 Jan;22 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.09.007. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016. PMID: 26350119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, et al. Mutation in the alpha‐synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science 1997;276:2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, et al. Alpha‐synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science 2003;302:841. - PubMed
-
- Chartier‐Harlin MC, Kachergus J, Roumier C, et al. Alpha‐synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet 2004;364:1167–1169. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

