Coronary Artery Dissection and Myocarditis Caused by Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA): A Case Report
- PMID: 37868681
- PMCID: PMC10589049
- DOI: 10.55729/2000-9666.1219
Coronary Artery Dissection and Myocarditis Caused by Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA): A Case Report
Abstract
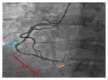
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) also referred to as Churg-Strauss syndrome is a rare vasculitis of the small to medium vessels. We present a rare case of acute coronary artery dissection brought on by EGPA, which generally has a poor prognosis. A 41-year-old male with history of bronchial asthma presented to the emergency room with a 2-week history of dyspnea, cough with clear phlegm, and fever. For the past eight months he had experienced episodes with similar symptoms relieved by steroids. CT chest showed bilateral upper lobe patchy opacities with extensive workup for infectious etiology being negative. He had peripheral eosinophilia with sinusitis. He had acute coronary syndrome and Coronary angiogram showed Right coronary artery dissection. After making a diagnosis of EGPA based on American college of Rheumatology criteria, he was successfully treated with high dose immunosuppression. Coronary artery dissection is a fatal and uncommon complication of EGPA which is usually diagnosed postmortem. Early recognition of this condition ante mortem and aggressive treatment can be lifesaving as demonstrated in our case.
Keywords: ANCA; Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; Churg-Strauss syndrome; Coronary artery vasculitis; EGPA; Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis; Glucocorticoids/therapeutic use; Granulomatosis with polyangiitis/diagnosis; Granulomatosis with polyangiitis/drug therapy; Humans; Immunosuppressive agents/therapeutic use; Vasculitis.
© 2023 Greater Baltimore Medical Center.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Torasemide-induced Vascular Purpura in the Course of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2022 Sep;30(2):116-118. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2022. PMID: 36254546
-
A Rare Geriatric Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Feb 24;15(2):e35398. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35398. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36846640 Free PMC article.
-
A rare case report of polyangiitis overlap syndrome: granulomatosis with polyangiitis and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis.BMC Pulm Med. 2018 Nov 29;18(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0733-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2018. PMID: 30497438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case Report: Middle lobe syndrome: a rare presentation in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 10;14:1222431. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1222431. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37638004 Free PMC article.
-
Churg-Strauss syndrome.Autoimmun Rev. 2015 Apr;14(4):341-8. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.12.004. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Autoimmun Rev. 2015. PMID: 25500434 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac Mass and Cerebrovascular Accident as Primary Manifestations of Churg-Strauss Syndrome.Arch Iran Med. 2023 Nov 1;26(11):662-664. doi: 10.34172/aim.2023.97. Arch Iran Med. 2023. PMID: 38310427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Comarmond C, Pagnoux C, Khellaf M, et al. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss): clinical characteristics and long-term followup of the 383 patients enrolled in the French Vasculitis Study Group cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Jan;65(1):270–281. doi: 10.1002/art.37721. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lin M, Su Z, Huang J, Li J, Luo N, Wang J. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis presenting with repetitive acute coronary syndrome, refractory coronary vasospasm, and spontaneous coronary dissection: a case report. J Int Med Res. 2022 Mar;50(3):3000605221089516. doi: 10.1177/03000605221089516. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous