Efficacy of avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib by numbers of IMDC risk factors and target tumor sites at baseline in advanced renal cell carcinoma: long-term follow-up results from JAVELIN Renal 101
- PMID: 37866029
- PMCID: PMC10774904
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.102034
Efficacy of avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib by numbers of IMDC risk factors and target tumor sites at baseline in advanced renal cell carcinoma: long-term follow-up results from JAVELIN Renal 101
Abstract
Background: In the phase III JAVELIN Renal 101 trial, first-line avelumab + axitinib improved progression-free survival (PFS) and objective response rate versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma across all International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium (IMDC) risk groups (favorable, intermediate, and poor); analyses of overall survival (OS) remain immature. Here, we report post hoc analyses of efficacy from the third interim analysis (data cut-off, April 2020) by the numbers of IMDC risk factors and target tumor sites at baseline.
Methods: Efficacy endpoints assessed were PFS, objective response, and best overall response per investigator assessment (RECIST v1.1) and OS. Best percentage change and percentage change from baseline in target tumor size over time during the study were also assessed.
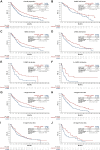
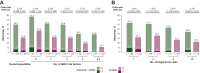
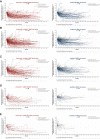
Results: In patients with 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4-6 IMDC risk factors, hazard ratios [HRs; 95% confidence interval (CIs)] for OS with avelumab + axitinib versus sunitinib were 0.660 (0.356-1.223), 0.745 (0.524-1.059), 0.973 (0.668-1.417), 0.718 (0.414-1.248), and 0.443 (0.237-0.829), and HRs (95% CIs) for PFS were 0.706 (0.490-1.016), 0.709 (0.540-0.933), 0.711 (0.527-0.960), 0.501 (0.293-0.854), and 0.395 (0.214-0.727), respectively. In patients with 1, 2, 3, or ≥4 target tumor sites, HRs (95% CIs) for OS with avelumab + axitinib versus sunitinib were 0.912 (0.640-1.299), 0.715 (0.507-1.006), 0.679 (0.442-1.044), and 0.747 (0.346-1.615), and HRs (95% CIs) for PFS were 0.706 (0.548-0.911), 0.552 (0.422-0.723), 0.856 (0.589-1.244), and 0.662 (0.329-1.332), respectively. Across all subgroups, analyses of objective response rate and complete response rate favored avelumab + axitinib versus sunitinib, and a greater proportion of patients treated with avelumab + axitinib had tumor shrinkage.
Conclusions: In post hoc analyses, first-line treatment with avelumab + axitinib was generally associated with efficacy benefits versus treatment with sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma across subgroups defined by different numbers of IMDC risk factors or target tumor sites.
Keywords: avelumab; axitinib; renal cell carcinoma; risk factor; tumor site.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure YT has participated in consulting or advisory roles for Eisai, Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD), and Ono Pharmaceutical; has received honoraria from Astellas Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb Japan, Chugai Pharma, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical, and Pfizer; and has received research funding from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharma, Eisai, MSD, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, and Takeda. RJM has participated in consulting or advisory roles for AstraZeneca, Aveo, Calithera Biosciences, Eisai, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Incyte, Pfizer, and EMD Serono Research & Development Institute, Inc., Billerica, MA, USA, an affiliate of Merck KGaA; has received travel, accommodations, and expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb; and has received research funding from Aveo, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, and EMD Serono Research & Development Institute, Inc., Billerica, MA, USA, an affiliate of Merck KGaA. TKC reports institutional and personal, paid and/or unpaid support for research, advisory boards, consultancy, and honoraria from Aravive, AstraZeneca, Aveo, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calithera, Circle Pharma, CME events (Peerview, OncLive, MJH and others), Eisai, EMD Serono Research & Development Institute, Inc., Billerica, MA, USA, an affiliate of Merck KGaA, Exelixis, GlaxoSmithKline, IQVA, Infinity, Ipsen, Jansen, Kanaph, Lilly, MSD, NiKang, Novartis, Nuscan, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi/Aventis, Surface Oncology, Takeda, Tempest, and Up-To-Date, outside the submitted work; reports institutional patents filed on molecular alterations and immunotherapy response/toxicity, and circulating tumor DNA; reports equity Osel, Pionyr, Precede Bio, and Tempest; has served in committees for ACCRU, ASCO/ESMO, GU Steering Committee, KidneyCan, and NCCN; reports that medical writing and editorial assistance support may have been funded by communications companies in part; has mentored several non-US citizens on research projects with potential funding (in part) from non-US sources/foreign components; reports that the institution (Dana-Farber Cancer Institute) may have received additional independent funding of drug companies or/and royalties potentially involved in research around the subject matter; and is supported in part by the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center Kidney SPORE (2P50CA101942-16) and Program 5P30CA006516-56, the Kohlberg Chair at Harvard Medical School and the Trust Family, Michael Brigham, Pan Mass Challenge, and Loker Pinard Funds for Kidney Cancer Research at DFCI. BIR has participated in consulting or advisory roles for 3D Medicines, Aravive, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Aveo, Bristol Myers Squibb, Corvus Pharmaceuticals, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, EMD Serono Research & Development Institute, Inc., Billerica, MA, USA, an affiliate of Merck KGaA, Shionogi, Surface Oncology, and Synthorx; reports leadership with MJH Life Sciences; has received travel, accommodations, and expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and EMD Serono Research & Development Institute, Inc., Billerica, MA, USA, an affiliate of Merck KGaA; reports stock and other ownership interests from PTC Therapeutics; and has received research funding from Aravive, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dragonfly Therapeutics, Immunomedics, Incyte, Exelixis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Seagen, Surface Oncology, Taris, and EMD Serono Research & Development Institute, Inc., Billerica, MA, USA, an affiliate of Merck KGaA. HM has received honoraria, consulting or advisory fees, and research funding from Pfizer. MO has participated in consulting or advisory roles for Bayer; has received honoraria from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb Japan, Chugai Pharma, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Takeda; and has received research funding from Astellas Pharma. LA has participated in consulting or advisory roles for Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bellerophon Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Corvus Pharmaceuticals, Eisai, Janssen, Ipsen, Merck, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; has received travel, accommodations, and expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb and MSD; and has received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb. MA is an employee of Pfizer R&D Japan. YU is an employee of Pfizer R&D Japan and holds stock in Pfizer. JW is an employee and reports stock and other ownership interest with Pfizer. AdiP reports employment, stock, and other ownership interest with Pfizer, and has received honoraria from Pfizer. MS has participated in consulting or advisory roles for Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, EUSA Pharma, Ipsen, MSD, and Roche; has received travel, accommodations, and expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb, Ipsen, and Roche; and has received honoraria from Alkermes, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, EUSA Pharma, Ipsen, Janssen Oncology, and MSD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extended follow-up from JAVELIN Renal 101: subgroup analysis of avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib by the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium risk group in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.ESMO Open. 2023 Jun;8(3):101210. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.101210. Epub 2023 Apr 25. ESMO Open. 2023. PMID: 37104931 Free PMC article.
-
Association of C-reactive protein with efficacy of avelumab plus axitinib in advanced renal cell carcinoma: long-term follow-up results from JAVELIN Renal 101.ESMO Open. 2022 Oct;7(5):100564. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100564. Epub 2022 Aug 28. ESMO Open. 2022. PMID: 36037566 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Avelumab plus axitinib vs sunitinib for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Japanese subgroup analysis from JAVELIN Renal 101.Cancer Sci. 2020 Mar;111(3):907-923. doi: 10.1111/cas.14294. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31883418 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Avelumab and axitinib in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma: safety and efficacy.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020 May;20(5):343-354. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2020.1756780. Epub 2020 May 7. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32293937 Review.
-
Axitinib, cabozantinib, everolimus, nivolumab, sunitinib and best supportive care in previously treated renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2018 Jan;22(6):1-278. doi: 10.3310/hta22060. Health Technol Assess. 2018. PMID: 29393024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Health Care Resource Use for Modern First-Line Treatments in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jul 1;7(7):e2422674. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.22674. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 39052293 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative systemic treatments in renal cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 May 21;14:1362172. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1362172. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38841158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- EUA Guidelines: renal cell carcinoma. https://uroweb.org/guideline/renal-cell-carcinoma/ Available at.
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Kidney cancer. Version 1. 2024. 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf
-
- Escudier B., Porta C., Schmidinger M., et al. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:706–720. - PubMed
-
- Powles T. Recent eUpdate to the ESMO clinical practice guidelines on renal cell carcinoma on cabozantinib and nivolumab for first-line clear cell renal cancer: renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:422–423. - PubMed
-
- Inlyta (axitinib) Pfizer.; 2022. Prescribing information.https://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=759 ; 2022. Available at.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

