Intestinal Tuft Cells: Morphology, Function, and Implications for Human Health
- PMID: 37863104
- PMCID: PMC11193883
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-042022-030310
Intestinal Tuft Cells: Morphology, Function, and Implications for Human Health
Abstract
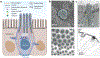
Tuft cells are a rare and morphologically distinct chemosensory cell type found throughout many organs, including the gastrointestinal tract. These cells were identified by their unique morphologies distinguished by large apical protrusions. Ultrastructural data have begun to describe the molecular underpinnings of their cytoskeletal features, and tuft cell-enriched cytoskeletal proteins have been identified, although the connection of tuft cell morphology to tuft cell functionality has not yet been established. Furthermore, tuft cells display variations in function and identity between and within tissues, leading to the delineation of distinct tuft cell populations. As a chemosensory cell type, they display receptors that are responsive to ligands specific for their environment. While many studies have demonstrated the tuft cell response to protists and helminths in the intestine, recent research has highlighted other roles of tuft cells as well as implicated tuft cells in other disease processes including inflammation, cancer, and viral infections. Here, we review the literature on the cytoskeletal structure of tuft cells. Additionally, we focus on new research discussing tuft cell lineage, ligand-receptor interactions, tuft cell tropism, and the role of tuft cells in intestinal disease. Finally, we discuss the implication of tuft cell-targeted therapies in human health and how the morphology of tuft cells may contribute to their functionality.
Keywords: chemosensation; cytoskeleton; differentiation; inflammation; microbiome; tuft cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advillin is a tuft cell marker in the mouse alimentary tract.J Mol Histol. 2020 Aug;51(4):421-435. doi: 10.1007/s10735-020-09893-6. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Mol Histol. 2020. PMID: 32617896 Free PMC article.
-
Colonic Tuft Cells: The Less-Recognized Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 5;25(11):6209. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116209. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interpreting heterogeneity in intestinal tuft cell structure and function.J Clin Invest. 2018 May 1;128(5):1711-1719. doi: 10.1172/JCI120330. Epub 2018 May 1. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29714721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tuft Cells and Their Role in Intestinal Diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 14;13:822867. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.822867. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35237268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dclk1-expressing tuft cells: critical modulators of the intestinal niche?Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017 Oct 1;313(4):G285-G299. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00073.2017. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28684459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tuft cells in the intestine, immunity and beyond.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Dec;21(12):852-868. doi: 10.1038/s41575-024-00978-1. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39327439 Review.
-
Epithelial-neuronal-immune cell interactions: Implications for immunity, inflammation, and tissue homeostasis at mucosal sites.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 May;153(5):1169-1180. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.02.004. Epub 2024 Feb 16. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38369030 Review.
-
Intestinal tuft cells act as reserve stem cells after injury.Nature. 2024 Oct 23. doi: 10.1038/d41586-024-03383-5. Online ahead of print. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39443763 No abstract available.
-
Clostridium sporogenes-derived metabolites protect mice against colonic inflammation.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2412669. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2412669. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39397690 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Tuft Cells Are Enriched With Protocadherins.J Histochem Cytochem. 2024 Oct;72(10):611-622. doi: 10.1369/00221554241287267. Epub 2024 Oct 3. J Histochem Cytochem. 2024. PMID: 39360911
References
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Morgan D, Raff M, et al. 2014. Molecular Biology of the Cell New York: Garland Sci.
-
- Peterson LW, Artis D. 2014. Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol 14:141–53 - PubMed
-
- Jarvi O,Keyrilainen O. 1956. On the cellular structures of the epithelial invasions in the glandular stomach of mice caused by intramural application of 20-methylcholantren. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. Suppl 39:72–73 - PubMed
-
- Rhodin J, Dalhamn T. 1956. Electron microscopy of the tracheal ciliated mucosa in rat. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat 44:345–412 - PubMed
-
- Järvi O 1962. A review of the part played by gastrointestinal heterotopias in neoplasmogenesis. Proc. Finn. Acad. Sci 1962:151–87
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

